Group-based randomized trial of contingencies for health and abstinence in HIV patients
- PMID: 20099954
- PMCID: PMC2813453
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016778
Group-based randomized trial of contingencies for health and abstinence in HIV patients
Abstract
Objective: Contingency management (CM) treatments are usually applied individually for drug abstinence, but CM can also be targeted toward health behaviors and implemented in groups. This study evaluated effects of a group-based CM intervention that focused on reinforcing health behaviors.
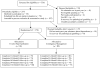
Method: HIV-positive patients with cocaine or opioid use disorders (n = 170) were randomized to weekly CM or 12-step (TS) groups for 24 weeks (mean attendance was 10.8 +/- 8.1 sessions for CM participants and 9.0 +/- 6.9 session for TS participants). During the treatment period, both groups received compensation for attendance ($10 per session) and submission of urine samples (about $2 per sample). In addition, participants received $25 for submitting samples and completing evaluations at Months 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12; 65-75 of the 81 participants assigned to TS and 71-80 of the 89 participants assigned to CM completed these evaluations. During the treatment period, patients in the CM group received chances to win prizes contingent upon completing health activities and submitting substance-free specimens (M = $260, SD = $267).
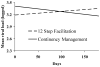
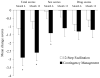
Results: Mean attendance was 10.8 +/- 8.1 sessions for CM participants and 9.0 +/- 6.9 sessions for TS participants. CM participants submitted a significantly greater number of consecutive drug-free specimens than did TS participants (5.2 +/- 6.0 vs. 3.7 +/- 5.6), but proportions of negative samples did not differ between groups during treatment or at follow-up evaluations. From pre- to posttreatment, CM participants showed greater reductions in viral loads and HIV-risk behaviors than did TS participants, but these effects were not maintained throughout the follow-up period.
Conclusions: These data suggest the efficacy of group-based CM for HIV-positive substance abusers, but more research is needed to extend the long-term benefits.
Figures

References
-
- Alessi SM, Hanson T, Wieners M, Petry NM. Low-cost contingency management in community clinics: delivering incentives partially in group therapy. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2007;15(3):293–300. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Appel PW, Ellison AA, Jansky HK, Oldak R. Barriers to enrollment in drug abuse treatment and suggestions for reducing them: opinions of drug injecting street outreach clients and other system stakeholders. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse. 2004;30(1):129–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA013444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AA07290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA021567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA13444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA14618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AA03510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA023918/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA09241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

