JWH018, a common constituent of 'Spice' herbal blends, is a potent and efficacious cannabinoid CB receptor agonist
- PMID: 20100276
- PMCID: PMC2931559
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00582.x
JWH018, a common constituent of 'Spice' herbal blends, is a potent and efficacious cannabinoid CB receptor agonist
Abstract
Background and purpose: 'Spice' is an herbal blend primarily marketed in Europe as a mild hallucinogen with prominent cannabis-like effects and as a legal alternative to cannabis. However, a recent report identified a number of synthetic additives in samples of 'Spice'. One of these, the indole derivative JWH018, is a ligand for the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB(1)) cannabinoid receptor and inhibits cAMP production in CB(1) receptor-expressing CHO cells. Other effects of JWH018 on CB(1) receptor-mediated signalling are not known, particularly in neurons. Here we have evaluated the signalling pathways activated by JWH018 at CB(1) receptors.
Experimental approach: We investigated the effects of JWH018 on neurotransmission in cultured autaptic hippocampal neurons. We further analysed its activation of ERK1/2 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and internalization of CB(1) receptors in HEK293 cells stably expressing this receptor.
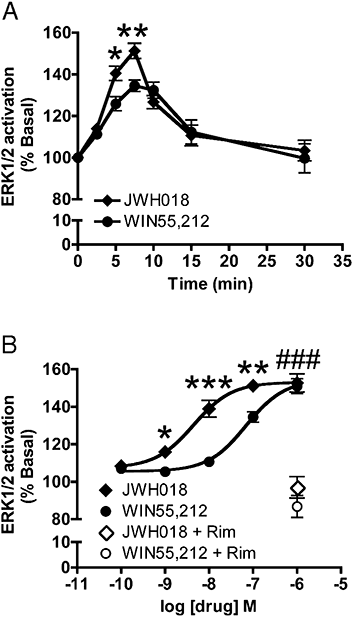
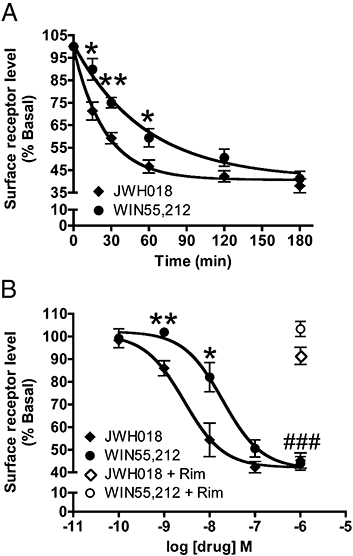
Key results: In cultured autaptic hippocampal neurons, JWH018 potently inhibited excitatory postsynaptic currents (IC(50)= 14.9 nM) in a concentration- and CB(1) receptor-dependent manner. Furthermore, it increased ERK1/2 MAPK phosphorylation (EC(50)= 4.4 nM). We also found that JWH018 potently induced rapid and robust CB(1) receptor internalization (EC(50)= 2.8 nM; t(1/2)= 17.3 min).
Conclusions and implications: JWH018, a prominent component of several herbal preparations marketed for their psychoactivity, is a potent and effective CB(1) receptor agonist that activates multiple CB(1) receptor signalling pathways. Thus, it is likely that the subjective effects of 'Spice' are due to activation of cannabinoid CB(1) receptors by JWH018, added to this herbal preparation.
Figures
References
-
- Aung MM, Griffin G, Huffman JW, Wu M, Keel C, Yang B, et al. Influence of the N-1 alkyl chain length of cannabimimetic indoles upon CB(1) and CB(2) receptor binding. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000;60:133–140. - PubMed
-
- Auwarter V, Dresen S, Weinmann W, Muller M, Putz M, Ferreiros N. ‘Spice’ and other herbal blends: harmless incense or cannabinoid designer drugs? J Mass Spectrom. 2009;44:832–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

