Improvement of myocardial perfusion reserve detected by cardiovascular magnetic resonance after direct endomyocardial implantation of autologous bone marrow cells in patients with severe coronary artery disease
- PMID: 20100336
- PMCID: PMC2845579
- DOI: 10.1186/1532-429X-12-6
Improvement of myocardial perfusion reserve detected by cardiovascular magnetic resonance after direct endomyocardial implantation of autologous bone marrow cells in patients with severe coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: Recent studies suggested that bone marrow (BM) cell implantation in patients with severe chronic coronary artery disease (CAD) resulted in modest improvement in symptoms and cardiac function. This study sought to investigate the functional changes that occur within the chronic human ischaemic myocardium after direct endomyocardial BM cells implantation by cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR).
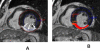
Methods and results: We compared the interval changes of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), myocardial perfusion reserve and the extent of myocardial scar by using late gadolinium enhancement CMR in 12 patients with severe CAD. CMR was performed at baseline and at 6 months after catheter-based direct endomyocardial autologous BM cell (n = 12) injection to viable ischaemic myocardium as guided by electromechanical mapping. In patients randomized to receive BM cell injection, there was significant decrease in percentage area of peri-infarct regions (-23.6%, P = 0.04) and increase in global LVEF (+9.0%, P = 0.02), the percentage of regional wall thickening (+13.1%, P= 0.04) and MPR (+0.25%, P = 0.03) over the target area at 6-months compared with baseline.
Conclusions: Direct endomyocardial implantation of autologous BM cells significantly improved global LVEF, regional wall thickening and myocardial perfusion reserve, and reduced percentage area of peri-infarct regions in patients with severe CAD.
Figures

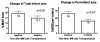
References
-
- Perin EC, Dohmann HF, Borojevic R, Silva SA, Sousa AL, Mesquita CT, Rossi MI, Carvalho AC, Dutra HS, Dohmann HJ, Silva GV, Belem L, Vivacqua R, Rangel FO, Esporcatte R, Geng YJ, Vaughn WK, Assad JA, Mesquita ET, Willerson JT. Transendocardial, autologous bone marrow cell transplantation for severe, chronic ischemic heart failure. Circulation. 2003;107:2294–2302. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000070596.30552.8B. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fuchs S, Satler LF, Kornowski R, Okubagzi P, Weisz G, Baffour R, Waksman R, Weissman NJ, Cerqueira M, Leon MB, Epstein SE. Catheter-based autologous bone marrow myocardial injection in no-option patients with advanced coronary artery disease. A feasibility study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:1721–1724. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00328-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Briguori C, Reimers B, Sarais C, Napodano M, Pascotto P, Azzarello G, Bregni M, Porcellini A, Vinante O, Zanco P, Peschle C, Condorelli G, Colombo A. Direct intramyocardial percutaneous delivery of autologous bone marrow in patients with refractory myocardial angina. Am Heart J. 2006;151:674–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2005.04.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beeres SL, Bax JJ, Kaandorp TA, Zeppenfeld K, Lamb HJ, Dibbets-Schneider P, Stokkel MP, Fibbe WE, de Roos A, Wall EE van der, Schalij MJ, Atsma DE. Usefulness of intramyocardial injection of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells in patients with severe angina pectoris and stress-induced myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97:1326–31. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.11.068. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

