Implication of the env gene of the human endogenous retrovirus W family in the expression of BDNF and DRD3 and development of recent-onset schizophrenia
- PMID: 20100784
- PMCID: PMC3160218
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbp166
Implication of the env gene of the human endogenous retrovirus W family in the expression of BDNF and DRD3 and development of recent-onset schizophrenia
Abstract
Objective: Retrovirus has been suggested as one of agents involved in the development of schizophrenia. In the present study, we examined the role of the human endogenous retrovirus W family (HERV-W) env gene in the etiopathogenesis of recent-onset schizophrenia, using molecular and epidemiological approaches.
Methods: Nested RT-PCR was used to detect the messenger RNA (mRNA) of the HERV-w env gene in plasmas. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was employed to detect the viral reverse transcriptase activity in human sera. Human U251 glioma cells were used to study the potential role of the HERV-W env gene in the etiopathogenesis of recent-onset schizophrenia.
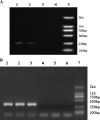
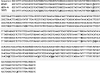
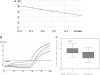
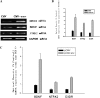
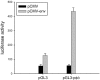
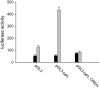
Results: We identified genes with mRNA sequences homologous to HERV-W env gene from plasmas of 42 out of 118 individuals with recent-onset schizophrenia but not from any of 106 normal persons (P < .01, t test). Quantitative real-time PCR showed a significantly increase in the reverse transcriptase activity in the sera of patients (by 35.59%) compared with controls (by 2.83%) (P < .05, t test). Overexpression of HERV-w env in human U251 glioma cells upregulated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), an important schizophrenia-associated gene, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2 (NTRK2, also called TrkB), and dopamine receptor D3 and increased the phosphorylation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding (CREB) protein. BDNF promoter reporter gene assays showed that the HERV-W env triggers BDNF production in human U251 glioma cells. Using gene knockdown, we found that CREB is required for the expression of BDNF that is regulated by env.
Conclusion: Our data revealed that the transcriptional activation of HERV is associated with the development of schizophrenia in some patients and indicated that HERV-W env regulates the expression of schizophrenia-associated genes. This report is the first to elucidate the signaling pathway responsible for the upregulation of HERV-W env-triggered BDNF. Our study provides new evidence for the involvement of HERV-W in the central nervous system, which will benefit the diagnosis and treatment of the devastating schizophrenia and related disorders.
Figures

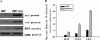
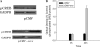


References
-
- Zhang WX, Shen YC, Li SR. Epidemiological survey on mental disorders in 7 areas in China. Chin J Psychiatry. 1998;31:69–71.
-
- Phillips MR, Yang GH, Li SR, Li Y. Suicide and the unique prevalence pattern of schizophrenia in mainland China: a retrospective observational study. Lancet. 2004;364:1062–1068. - PubMed
-
- Lewis DA, Lieberman JA. Catching up on schizophrenia: natural history and neurobiology. Neuron. 2000;28:325–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

