The novel mouse Polo-like kinase 5 responds to DNA damage and localizes in the nucleolus
- PMID: 20100802
- PMCID: PMC2875007
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq011
The novel mouse Polo-like kinase 5 responds to DNA damage and localizes in the nucleolus
Abstract
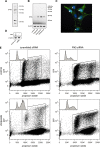
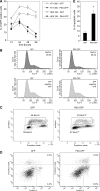
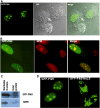
Polo-like kinases (Plk1-4) are emerging as an important class of proteins involved in many aspects of cell cycle regulation and response to DNA damage. Here, we report the cloning of a fifth member of the polo-like kinase family named Plk5. DNA and protein sequence analyses show that Plk5 shares more similarities with Plk2 and Plk3 than with Plk1 and Plk4. Consistent with this observation, we show that mouse Plk5 is a DNA damage inducible gene. Mouse Plk5 protein localizes predominantly to the nucleolus, and deletion of a putative nucleolus localization signal (NoLS) within its N-terminal moiety disrupts its nucleolar localization. Ectopic expression of Plk5 leads to cell cycle arrest in G1, decreased DNA synthesis, and to apoptosis, a characteristic it shares with Plk3. Interestingly, in contrast to mouse Plk5 gene, the sequence of human Plk5 contains a stop codon that produces a truncated protein lacking part of the kinase domain.
Figures

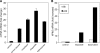
References
-
- Logarinho E, Sunkel CE. The Drosophila POLO kinase localises to multiple compartments of the mitotic apparatus and is required for the phosphorylation of MPM2 reactive epitopes. J. Cell Sci. 1998;111(Pt 19):2897–2909. - PubMed
-
- Moutinho-Santos T, Sampaio P, Amorim I, Costa M, Sunkel CE. In vivo localisation of the mitotic POLO kinase shows a highly dynamic association with the mitotic apparatus during early embryogenesis in Drosophila. Biol. Cell. 1999;91:585–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

