The mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain V-D intergenic sequence contains insulators that may regulate ordered V(D)J recombination
- PMID: 20100833
- PMCID: PMC2843181
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098251
The mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain V-D intergenic sequence contains insulators that may regulate ordered V(D)J recombination
Abstract
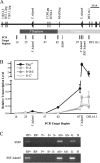
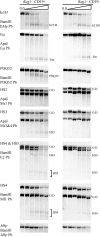
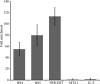
During immunoglobulin heavy chain (Igh) V(D)J recombination, D to J precedes V to DJ recombination in an ordered manner, controlled by differential chromatin accessibility of the V and DJ regions and essential for correct antibody assembly. However, with the exception of the intronic enhancer Emu, which regulates D to J recombination, cis-acting regulatory elements have not been identified. We have assembled the sequence of a strategically located 96-kb V-D intergenic region in the mouse Igh and analyzed its activity during lymphocyte development. We show that Emu-dependent D antisense transcription, proposed to open chromatin before D to J recombination, extends into the V-D region for more than 30 kb in B cells before, during, and after V(D)J recombination and in T cells but terminates 40 kb from the first V gene. Thus, subsequent V antisense transcription before V to DJ recombination is actively prevented and must be independently activated. To find cis-acting elements that regulate this differential chromatin opening, we identified six DNase I-hypersensitive sites (HSs) in the V-D region. One conserved HS upstream of the first D gene locally regulates D genes. Two further conserved HSs near the D region mark a sharp decrease in antisense transcription, and both HSs bind CTCF in vivo. Further, they both possess enhancer-blocking activity in vivo. Thus, we propose that they are enhancer-blocking insulators preventing Emu-dependent chromatin opening extending into the V region. Thus, they are the first elements identified that may control ordered V(D)J recombination and correct assembly of antibody genes.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

