Broad-spectrum activity against bacterial mastitis pathogens and activation of mammary epithelial cells support a protective role of neutrophil cathelicidins in bovine mastitis
- PMID: 20100862
- PMCID: PMC2849419
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01090-09
Broad-spectrum activity against bacterial mastitis pathogens and activation of mammary epithelial cells support a protective role of neutrophil cathelicidins in bovine mastitis
Abstract
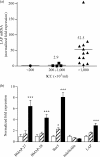
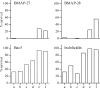
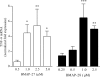
Cathelicidins are peptide components of the innate immune system of mammals. Apart from exerting a direct antibiotic activity, they can also trigger specific defense responses in the host. Their roles in various pathophysiological conditions have been studied, but there is a lack of published information on their expression and activities in the context of mastitis. The aims of this study were to investigate the expression of the bovine cathelicidins BMAP-27, BMAP-28, Bac5, and indolicidin in healthy and infected mammary tissue and in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated cells, to determine their activities against bacteria isolated from bovine mastitis, and to examine their potentials to trigger defense responses in bovine mammary cells. The genes were found to be upregulated in LPS-stimulated neutrophils, but not in infected quarters or epithelial cells. All peptides showed a variably broad spectrum of activity against 28 bacterial isolates from bovine mastitis (MIC values, 0.5 to 32 microM), some of which were antibiotic resistant. The activity of each peptide was significantly enhanced when it was pairwise tested with the other peptides, reaching the synergy threshold when indolicidin was present. The bactericidal activity was sensitive to milk components; BMAP-27 and -28 were highly effective in mastitic bovine milk and inhibited in milk from healthy cows. Both peptides were also active in whey and in blood serum and triggered the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Our results indicate multiple roles for the bovine cathelicidins in mastitis, with complementary and mutually enhanced antimicrobial activities against causative pathogens and the capacity to activate host cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host defense cathelicidins in cattle: types, production, bioactive functions and potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Jun;51(6):813-821. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29476808 Review.
-
Cathelicidin production and release by mammary epithelial cells during infectious mastitis.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017 Jul;189:66-70. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28669389
-
Expression of cathelicidins mRNA in the goat mammary gland and effect of the intramammary infusion of lipopolysaccharide on milk cathelicidin-2 concentration.Vet Microbiol. 2014 May 14;170(1-2):125-34. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.01.029. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24572177
-
Transcriptomics and iTRAQ-Proteomics Analyses of Bovine Mammary Tissue with Streptococcus agalactiae-Induced Mastitis.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Oct 24;66(42):11188-11196. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02386. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30096236
-
Defense of the bovine mammary gland by polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2002 Apr;7(2):109-21. doi: 10.1023/a:1020343717817. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2002. PMID: 12463734 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative secretome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus strains with different within-herd intramammary infection prevalence.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):174-190. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2024014. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35030987 Free PMC article.
-
Murine and Human Cathelicidins Contribute Differently to Hallmarks of Mastitis Induced by Pathogenic Prototheca bovis Algae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Feb 7;10:31. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00031. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117805 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of recombinant bovine epidermal growth factor in the treatment of experimental subclinical Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in a ewe model.Vet Rec Open. 2017 May 1;4(1):e000179. doi: 10.1136/vetreco-2016-000179. eCollection 2017. Vet Rec Open. 2017. PMID: 28761665 Free PMC article.
-
Cathelicidins: family of antimicrobial peptides. A review.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Dec;39(12):10957-70. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1997-x. Epub 2012 Oct 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 23065264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early immune innate hallmarks and microbiome changes across the gut during Escherichia coli O157: H7 infection in cattle.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):21535. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78752-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33299023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antcheva, N., F. Morgera, L. Creatti, L. Vaccari, U. Pag, S. Pacor, Y. Shai, H. G. Sahl, and A. Tossi. 2009. Artificial beta-defensin based on a minimal defensin template. Biochem. J. 421:435-447. - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi, I., J. N. Buffoni, and M. Feligini. 2009. Quantification of bovine casein fractions by direct chromatographic analysis of milk. Approaching the application to a real production context. J. Chromatogr. A 1216:165-168. - PubMed
-
- Chockalingam, A., D. S. Zarlenga, and D. D. Bannerman. 2007. Antimicrobial activity of bovine bactericidal permeability-increasing protein-derived peptides against gram-negative bacteria isolated from the milk of cows with clinical mastitis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 68:1151-1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

