The SLIT-ROBO pathway: a regulator of cell function with implications for the reproductive system
- PMID: 20100881
- PMCID: PMC2971463
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-10-0017
The SLIT-ROBO pathway: a regulator of cell function with implications for the reproductive system
Abstract
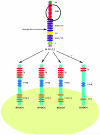
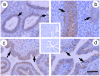
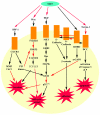
The secreted SLIT glycoproteins and their Roundabout (ROBO) receptors were originally identified as important axon guidance molecules. They function as a repulsive cue with an evolutionarily conserved role in preventing axons from migrating to inappropriate locations during the assembly of the nervous system. In addition the SLIT-ROBO interaction is involved in the regulation of cell migration, cell death and angiogenesis and, as such, has a pivotal role during the development of other tissues such as the lung, kidney, liver and breast. The cellular functions that the SLIT/ROBO pathway controls during tissue morphogenesis are processes that are dysregulated during cancer development. Therefore inactivation of certain SLITs and ROBOs is associated with advanced tumour formation and progression in disparate tissues. Recent research has indicated that the SLIT/ROBO pathway could also have important functions in the reproductive system. The fetal ovary expresses most members of the SLIT and ROBO families. The SLITs and ROBOs also appear to be regulated by steroid hormones and regulate physiological cell functions in adult reproductive tissues such as the ovary and endometrium. Furthermore several SLITs and ROBOs are aberrantly expressed during the development of ovarian, endometrial, cervical and prostate cancer. This review will examine the roles this pathway could have in the development, physiology and pathology of the reproductive system and highlight areas for future research that could further dissect the influence of the SLIT/ROBO pathway in reproduction.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews W, Barber M, Hernadez-Miranda LR, Xian J, Rakic S, Sundaresan V, Rabbitts TH, Pannell R, Rabbitts P, Thompson H, et al. The role of Slit-Robo signaling in the generation, migration and morphological differentiation of cortical interneurons. Developmental Biology. 2008;313:648–58. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw GJ, Kidd T, Murray D, Pawson T, Goodman CS. Repulsive axon guidance: Abelson and Enabled play opposing roles downstream of the roundabout receptor. Cell. 2000;101:703–15. - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell. 1999;96:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Chédotal A, Kerjan G, Moreau-Fauvarque C. The brain within the tumor: new roles for axon guidance molecules in cancers. Cell Death and Differentiation. 2005;12:1044–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

