A genomewide RNA interference screen for modifiers of aggregates formation by mutant Huntingtin in Drosophila
- PMID: 20100940
- PMCID: PMC2865916
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.112516
A genomewide RNA interference screen for modifiers of aggregates formation by mutant Huntingtin in Drosophila
Abstract
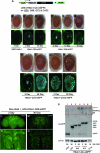
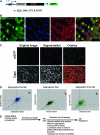
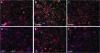
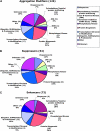
Protein aggregates are a common pathological feature of most neurodegenerative diseases (NDs). Understanding their formation and regulation will help clarify their controversial roles in disease pathogenesis. To date, there have been few systematic studies of aggregates formation in Drosophila, a model organism that has been applied extensively in modeling NDs and screening for toxicity modifiers. We generated transgenic fly lines that express enhanced-GFP-tagged mutant Huntingtin (Htt) fragments with different lengths of polyglutamine (polyQ) tract and showed that these Htt mutants develop protein aggregates in a polyQ-length- and age-dependent manner in Drosophila. To identify central regulators of protein aggregation, we further generated stable Drosophila cell lines expressing these Htt mutants and also established a cell-based quantitative assay that allows automated measurement of aggregates within cells. We then performed a genomewide RNA interference screen for regulators of mutant Htt aggregation and isolated 126 genes involved in diverse cellular processes. Interestingly, although our screen focused only on mutant Htt aggregation, several of the identified candidates were known previously as toxicity modifiers of NDs. Moreover, modulating the in vivo activity of hsp110 (CG6603) or tra1, two hits from the screen, affects neurodegeneration in a dose-dependent manner in a Drosophila model of Huntington's disease. Thus, other aggregates regulators isolated in our screen may identify additional genes involved in the protein-folding pathway and neurotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Andrew, S. E., Y. P. Goldberg, B. Kremer, H. Telenius, J. Theilmann et al., 1993. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington's disease. Nat. Genet. 4 398–403. - PubMed
-
- Arrasate, M., S. Mitra, E. S. Schweitzer, M. R. Segal and S. Finkbeiner, 2004. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature 431 805–810. - PubMed
-
- Bilen, J., and N. M. Bonini, 2005. Drosophila as a model for human neurodegenerative disease. Annu. Rev. Genet. 39 153–171. - PubMed
-
- Boutros, M., A. A. Kiger, S. Armknecht, K. Kerr, M. Hild et al., 2004. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of growth and viability in Drosophila cells. Science 303 832–835. - PubMed
-
- Brand, A. H., and N. Perrimon, 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118 401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

