Light-evoked NMDA receptor-mediated currents are reduced by blocking D-serine synthesis in the salamander retina
- PMID: 20101193
- PMCID: PMC2909446
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32833313b7
Light-evoked NMDA receptor-mediated currents are reduced by blocking D-serine synthesis in the salamander retina
Abstract
Experiments were carried out in the retina of the tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) to evaluate the importance of D-serine synthesis on light-evoked N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated components of ganglion cells and contributions to the proximal negative field potential. We blocked the synthesis of D-serine through brief exposures of the retina to phenazine ethosulfate and validated the changes in the tissue levels of D-serine using capillary electrophoresis methods to separate and measure the amino acid enantiomers. Ten minute exposures to phenazine ethosulfate decreased D-serine levels in the retina by about 50% and significantly reduced the NMDA receptor contribution to light responses of the inner retina. This is the first report of a linkage between D-serine synthesis and NMDA receptor activity in the vertebrate retina.
Figures

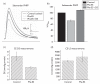
References
-
- Gustafson EC, Stevens ER, Wolosker H, Miller RF. Endogenous d-serine contributes to NMDA-receptor-mediated light-evoked responses in the vertebrate retina. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:122–130. - PubMed
-
- Dun Y, Duplantier J, Roon P, Martin PM, Ganapathy V, Smith SB. Serine racemase expression and d-serine content are developmentally regulated in neuronal ganglion cells of the retina. J Neurochem. 2008;104:970–978. - PubMed
-
- Diaz CM, Macnab LT, Williams SM, Sullivan RK, Pow DV. EAAT1 and d-serine expression are early features of human retinal development. Exp Eye Res. 2007;84:876–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

