Phosphorylation of the mutant K303R estrogen receptor alpha at serine 305 affects aromatase inhibitor sensitivity
- PMID: 20101208
- PMCID: PMC2922934
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.520
Phosphorylation of the mutant K303R estrogen receptor alpha at serine 305 affects aromatase inhibitor sensitivity
Abstract
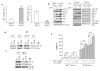
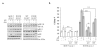
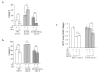
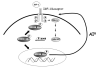
We earlier identified a lysine to arginine transition at residue 303 (K303R) in estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) in invasive breast cancers, which confers resistance to the aromatase inhibitor (AI) anastrozole (Ana) when expressed in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Here, we show that AI resistance arises through an enhanced cross talk of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R)/insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1/Akt pathway with ERalpha, and the serine (S) residue 305 adjacent to the K303R mutation has a key function in mediating this cross talk. The ERalpha S305 residue is an important site that modifies response to tamoxifen; thus, we questioned whether this site could also influence AI response. We generated stable transfectants-expressing wild-type, K303R ERalpha or a double K303R/S305A mutant receptor, and found that the AI-resistant phenotype associated with expression of the K303R mutation was dependent on activation of S305 within the receptor. Ana significantly reduced growth in K303R/S305A-expressing cells. Preventing S305 phosphorylation with a blocking peptide inhibited IGF-1R/IRS-1/Akt activation and also restored AI sensitivity. Our data suggest that the K303R mutation and the S305 ERalpha residue may be a novel determinant of AI response in breast cancer, and blockade of S305 phosphorylation represents a new therapeutic strategy for treating tumors resistant to hormone therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Agoulnik IU, Tong XW, Fischer DC, Korner K, Atkinson NE, Edwards DP, et al. A germline variation in the progesterone receptor gene increases transcriptional activity and may modify ovarian cancer risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:6340–7. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL, Osborne CK. Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res. 1989;49:6237–41. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

