Myc proteins as therapeutic targets
- PMID: 20101214
- PMCID: PMC2904682
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.512
Myc proteins as therapeutic targets
Abstract
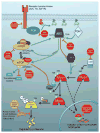
Myc proteins (c-myc, Mycn and Mycl) target proliferative and apoptotic pathways vital for progression in cancer. Amplification of the MYCN gene has emerged as one of the clearest indicators of aggressive and chemotherapy-refractory disease in children with neuroblastoma, the most common extracranial solid tumor of childhood. Phosphorylation and ubiquitin-mediated modulation of Myc protein influence stability and represent potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Phosphorylation of Myc proteins is controlled in-part by the receptor tyrosine kinase/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling, with additional contributions from Aurora A kinase. Myc proteins regulate apoptosis in part through interactions with the p53/Mdm2/Arf signaling pathway. Mutation in p53 is commonly observed in patients with relapsed neuroblastoma, contributing to both biology and therapeutic resistance. This review examines Myc function and regulation in neuroblastoma, and discusses emerging therapies that target Mycn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The p53 regulatory gene MDM2 is a direct transcriptional target of MYCN in neuroblastoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 18;102(3):731-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405495102. Epub 2005 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15644444 Free PMC article.
-
The MDM2 inhibitor CGM097 combined with the BET inhibitor OTX015 induces cell death and inhibits tumor growth in models of neuroblastoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(21):8144-8158. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3407. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 33034426 Free PMC article.
-
S(+)-ibuprofen destabilizes MYC/MYCN and AKT, increases p53 expression, and induces unfolded protein response and favorable phenotype in neuroblastoma cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jan;44(1):35-43. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2148. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24173829 Free PMC article.
-
The MYCN oncogene and differentiation in neuroblastoma.Semin Cancer Biol. 2011 Oct;21(4):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011. PMID: 21849159 Review.
-
The p53 pathway and its inactivation in neuroblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2003 Jul 18;197(1-2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00088-0. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 12880966 Review.
Cited by
-
Nobiletin Enhances Chemosensitivity to Adriamycin through Modulation of the Akt/GSK3β/β⁻Catenin/MYCN/MRP1 Signaling Pathway in A549 Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 26;10(12):1829. doi: 10.3390/nu10121829. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30486290 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation with High or Low Iron Reduces Colitis Severity in an AOM/DSS Mouse Model.Nutrients. 2022 May 12;14(10):2033. doi: 10.3390/nu14102033. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35631174 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of erythromycin on human neuroblastoma cell line (SH-SY5Y).J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Feb;31(1):33-38. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0146-4. Epub 2011 Feb 19. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21336720
-
Genetic instability and recurrent MYC amplification in ALK-translocated NSCLC: a central role of TP53 mutations.J Pathol. 2018 Sep;246(1):67-76. doi: 10.1002/path.5110. Epub 2018 Jul 31. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29885057 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of F-box proteins and its consequence on cancer development, progression and metastasis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2016 Feb;36:33-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.015. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016. PMID: 26432751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alaminos M, Mora J, Cheung N-KV, Smith A, Qin J, Chen L, et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression associated with MYCN in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4538–4546. - PubMed
-
- Amati B, Dalton S, Brooks MW, Littlewood TD, Evan GI, Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992;359:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Amente S, Gargano B, Diolaiti D, Della Valle G, Lania L, Majello B. p14ARF interacts with N-Myc and inhibits its transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:821–825. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong BC, Krystal GW. Isolation and characterization of complementary DNA for N-cym, a gene encoded by the DNA strand opposite to N-myc. Cell Growth Differ. 1992;3:385–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

