AT7519, A novel small molecule multi-cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma via GSK-3beta activation and RNA polymerase II inhibition
- PMID: 20101221
- PMCID: PMC3183744
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.510
AT7519, A novel small molecule multi-cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma via GSK-3beta activation and RNA polymerase II inhibition
Abstract
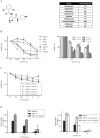
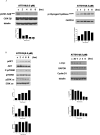
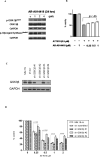
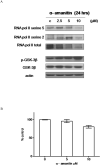
Dysregulated cell cycling is a universal hallmark of cancer and is often mediated by abnormal activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their cyclin partners. Overexpression of individual complexes are reported in multiple myeloma (MM), making them attractive therapeutic targets. In this study, we investigate the preclinical activity of a novel small-molecule multi-CDK inhibitor, AT7519, in MM. We show the anti-MM activity of AT7519 displaying potent cytotoxicity and apoptosis; associated with in vivo tumor growth inhibition and prolonged survival. At the molecular level, AT7519 inhibited RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) phosphorylation, a CDK9, 7 substrate, associated with decreased RNA synthesis confirmed by [(3)H] Uridine incorporation. In addition, AT7519 inhibited glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK-3beta) phosphorylation; conversely pretreatment with a selective GSK-3 inhibitor and shRNA GSK-3beta knockdown restored MM survival, suggesting the involvement of GSK-3beta in AT7519-induced apoptosis. GSK-3beta activation was independent of RNA pol II dephosphorylation confirmed by alpha-amanitin, a specific RNA pol II inihibitor, showing potent inhibition of RNA pol II phosphorylation without corresponding effects on GSK-3beta phosphorylation. These results offer new insights into the crucial, yet controversial role of GSK-3beta in MM and show significant anti-MM activity of AT7519, providing the rationale for its clinical evaluation in MM.
Figures


References
-
- Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:6333–6338. - PubMed
-
- Bhat R, Xue YF, Berg S, Hellberg S, Ormo M, Nilsson Y, Radesater AC, Jerning E, Markgren PO, Borgegard T, Nylof M, Gimenez-Cassina A, Hernandez F, Lucas JJ, Diaz-Nido J, Avila J. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:45937–45945. - PubMed
-
- Cai DP, Latham VM, Zhang XX, Shapiro GI. Cancer Research. 2006;66:9270–9280. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan D, Kharbanda S, Ogata A, Urashima M, Teoh G, Robertson M, Kufe DW, Anderson KC. Blood. 1997;89:227–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

