ARF-induced downregulation of Mip130/LIN-9 protein levels mediates a positive feedback that leads to increased expression of p16Ink4a and p19Arf
- PMID: 20101237
- PMCID: PMC4116813
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.485
ARF-induced downregulation of Mip130/LIN-9 protein levels mediates a positive feedback that leads to increased expression of p16Ink4a and p19Arf
Abstract
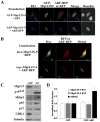
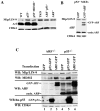
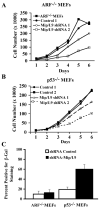
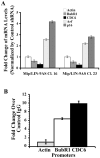
The ARF-MDM2-p53 pathway constitutes one of the most important mechanisms of surveillance against oncogenic transformation, and its inactivation occurs in a large proportion of cancers. Here, we show that ARF regulates Mip130/LIN-9 by inducing its translocation to the nucleolus and decreasing the expression of the Mip130/LIN-9 protein through a post-transcriptional mechanism. The knockdown of Mip130/LIN-9 in p53(-/-) and Arf(-/-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) mimics some effects of ARF, such as the downregulation of B-Myb, impaired induction of G2/M genes, and a decrease in cell proliferation. Importantly, although the knockdown of Mip130/LIN-9 reduced the proliferation of p53 or Arf-null MEFs, only p53(-/-) MEFs showed a senescence-like state and an increase in the expression of Arf and p16. Interestingly, the increase in p16 and ARF is indirect because the Mip130/LIN-9 knockdown decreased the transcription of negative regulators of the Ink4a/Arf locus, such as BUBR1 and CDC6. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays also reveal that Mip130/LIN-9 occupies the promoters of the BubR1 and cdc6 genes, suggesting that Mip130/LIN-9 is necessary for the expression of these genes. Altogether, these results indicate that there is a feedback mechanism between ARF and Mip130/LIN-9 in which either the increase of ARF or the decrease in Mip130/LIN-9 causes a further increase in the expression of Arf and p16.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

