Probiotics and gut health: a special focus on liver diseases
- PMID: 20101763
- PMCID: PMC2811790
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i4.403
Probiotics and gut health: a special focus on liver diseases
Abstract
Probiotic bacteria have well-established beneficial effects in the management of diarrhoeal diseases. Newer evidence suggests that probiotics have the potential to reduce the risk of developing inflammatory bowel diseases and intestinal bacterial overgrowth after gut surgery. In liver health, the main benefits of probiotics might occur through preventing the production and/or uptake of lipopolysaccharides in the gut, and therefore reducing levels of low-grade inflammation. Specific immune stimulation by probiotics through processes involving dendritic cells might also be beneficial to the host immunological status and help prevent pathogen translocation. Hepatic fat metabolism also seems to be influenced by the presence of commensal bacteria, and potentially by probiotics; although the mechanisms by which probiotic might act on the liver are still unclear. However, this might be of major importance in the future because low-grade inflammation, hepatic fat infiltration, and hepatitis might become more prevalent as a result of high fat intake and the increased prevalence of obesity.
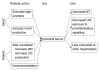
Figures
References
-
- Ouwehand AC. Antiallergic effects of probiotics. J Nutr. 2007;137:794S–797S. - PubMed
-
- Cummings JH, Antoine JM, Azpiroz F, Bourdet-Sicard R, Brandtzaeg P, Calder PC, Gibson GR, Guarner F, Isolauri E, Pannemans D, et al. PASSCLAIM--gut health and immunity. Eur J Nutr. 2004;43 Suppl 2:II118–II173. - PubMed
-
- Caballero-Franco C, Keller K, De Simone C, Chadee K. The VSL#3 probiotic formula induces mucin gene expression and secretion in colonic epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;292:G315–G322. - PubMed
-
- Otte JM, Podolsky DK. Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G613–G626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

