Hyperpolarized 89Y complexes as pH sensitive NMR probes
- PMID: 20102196
- PMCID: PMC2848490
- DOI: 10.1021/ja910278e
Hyperpolarized 89Y complexes as pH sensitive NMR probes
Abstract
Hyperpolarization can increase the sensitivity of NMR/MRI experiments, but the primary limitation is the T(1) decay of magnetization. Due to its long T(1), the hyperpolarized (89)Y nucleus makes an excellent candidate as an in vivo spectroscopy/imaging probe. Here we report the (89)Y chemical shift dependence upon pH for two hyperpolarized (89)Y(III) complexes and demonstrate how such complexes can be used as sensitive spectroscopy/imaging agents to measure pH.
Figures
 ) and YDO3A-NTs (
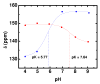
) and YDO3A-NTs ( ) as a function of pH (9.4 T and 25°C). The YDOTP data were collected from a single sample adjusted to different pH values after hyperpolarization while the YDO3A-NTs data required collection on different hyperpolarized samples due to rapid relaxation.
) as a function of pH (9.4 T and 25°C). The YDOTP data were collected from a single sample adjusted to different pH values after hyperpolarization while the YDO3A-NTs data required collection on different hyperpolarized samples due to rapid relaxation.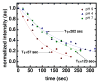
 ), 7 (
), 7 ( ), and 9 (
), and 9 ( ), with n=2 and an error of approximately ±10 sec.
), with n=2 and an error of approximately ±10 sec.Similar articles
-
Hyperpolarized 89Y-EDTMP complex as a chemical shift-based NMR sensor for pH at the physiological range.J Magn Reson. 2020 Nov;320:106837. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2020.106837. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Magn Reson. 2020. PMID: 33039915 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of yttrium-ligand complexation monitored using hyperpolarized (89)Y as a model for gadolinium in contrast agents.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Apr 14;132(14):5006-7. doi: 10.1021/ja1013954. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20302339
-
1H,89Y HMQC and further NMR spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction investigations on yttrium-containing complexes exhibiting various nuclearities.Chemistry. 2012 Apr 23;18(17):5325-34. doi: 10.1002/chem.201102636. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Chemistry. 2012. PMID: 22422575
-
Design of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Molecular Probes for Hyperpolarized Bioimaging.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Jun 25;60(27):14779-14799. doi: 10.1002/anie.201915718. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 32372551 Review.
-
Hyperpolarized NMR probes for biological assays.Sensors (Basel). 2014 Jan 16;14(1):1576-97. doi: 10.3390/s140101576. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24441771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous imaging of 13C metabolism and 1H structure: technical considerations and potential applications.NMR Biomed. 2015 May;28(5):576-82. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3279. Epub 2015 Mar 25. NMR Biomed. 2015. PMID: 25810146 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphonic acid: preparation and applications.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2017 Oct 20;13:2186-2213. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.13.219. eCollection 2017. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2017. PMID: 29114326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hydrogen peroxide-responsive hyperpolarized 13C MRI contrast agent.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Mar 23;133(11):3776-9. doi: 10.1021/ja111589a. Epub 2011 Mar 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21366297 Free PMC article.
-
The role of responsive MRI probes in the past and the future of molecular imaging.Chem Sci. 2024 Nov 27;15(48):20122-20154. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04849k. eCollection 2024 Dec 11. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39611034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship between NMR Chemical Shifts of Thermally Polarized and Hyperpolarized 89 Y Complexes and Their Solution Structures.Chemistry. 2016 Nov 7;22(46):16657-16667. doi: 10.1002/chem.201602901. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Chemistry. 2016. PMID: 27723138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallagher FA, Kettunen MI, Brindle KM. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 2009;55:285–295.
-
- Hsu PP, Sabatini DM. Cell. 2008;134:703–707. - PubMed
-
- van Sluis R, Bhujwalla ZM, Raghunand N, Ballesteros P, Alvarez J, Cerdán S, Galons JP, Gillies RJ. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41:743–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

