Binding of Munc18-1 to synaptobrevin and to the SNARE four-helix bundle
- PMID: 20102228
- PMCID: PMC2834481
- DOI: 10.1021/bi9021878
Binding of Munc18-1 to synaptobrevin and to the SNARE four-helix bundle
Abstract
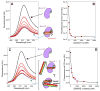
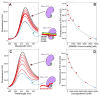
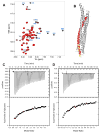
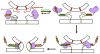
Sec1/Munc18 (SM) proteins and soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) form part of the core intracellular membrane fusion machinery, but it is unclear how they cooperate in membrane fusion. The synaptic vesicle SNARE synaptobrevin and the plasma membrane SNAREs syntaxin-1 and SNAP-25 assemble into a tight SNARE complex that includes a four-helix bundle formed by their SNARE motifs and is key for fusion. The neuronal SM protein Munc18-1 binds to syntaxin-1 and to the SNARE complex through interactions with the syntaxin-1 N-terminal region that are critical for neurotransmitter release. It has been proposed that Munc18-1 also binds to synaptobrevin and to the SNARE four-helix bundle and that such interactions might be crucial for membrane fusion, but definitive, direct evidence of these interactions has not been described. Using diverse biophysical approaches, we now demonstrate that Munc18-1 indeed binds to synaptobrevin and to the SNARE four-helix bundle. Both interactions have similar affinities (in the low micromolar range) and appear to involve the same cavity of Munc18-1 that binds to syntaxin-1. Correspondingly, the N-terminal region of syntaxin-1 competes with the SNARE four-helix bundle and synaptobrevin for Munc18-1 binding. Importantly, the Munc18-1 binding site on synaptobrevin is located at the C-terminus of its SNARE motif, suggesting that this interaction places Munc18-1 right at the site where fusion occurs. These results suggest a model in which neurotransmitter release involves a sequence of three different types of Munc18-1-SNARE interactions and in which Munc18-1 plays a direct, active role in membrane fusion in cooperation with the SNAREs.
Figures

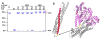
References
-
- Jahn R, Scheller RH. SNAREs--engines for membrane fusion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:631–643. - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT. Structure and function of SNARE and SNARE-interacting proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 2005:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Sudhof TC. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509–547. - PubMed
-
- Verhage M, Toonen RF. Regulated exocytosis: merging ideas on fusing membranes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:402–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

