Myriocin-mediated up-regulation of hepatocyte apoA-I synthesis is associated with ERK inhibition
- PMID: 20102334
- PMCID: PMC2860698
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20090452
Myriocin-mediated up-regulation of hepatocyte apoA-I synthesis is associated with ERK inhibition
Abstract
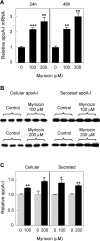
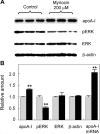
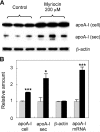
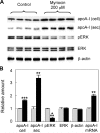
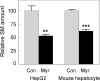
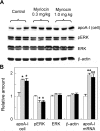
Sphingolipids including sphingomyelin have been implicated as potential atherogenic lipids. Studies in apoE (apolipoprotein E)-null mice have revealed that the serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor myriocin reduces plasma levels of sphingomyelin, ceramide, sphingosine-1-phosphate and glycosphingolipids and that this is associated with potent inhibition of atherosclerosis. Interestingly, hepatic apoA-I (apolipoprotein A-I) synthesis and plasma HDL (high-density lipoprotein)-cholesterol levels were also increased in apoE-null mice treated with myriocin. Since myriocin is a known inhibitor of ERK (extracellular-signal-related kinase) phosphorylation, we assessed the possibility that myriocin may be acting to increase hepatic apoA-I production via this pathway. To address this, HepG2 cells and primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with 200 muM myriocin for up to 48 h. Myriocin increased apoA-I mRNA and protein levels by approx. 3- and 2-fold respectively. Myriocin also increased apoA-I secretion up to 3.5-fold and decreased ERK phosphorylation by approx. 70%. Similar findings were obtained when primary hepatocytes were isolated from apoE-null mice that were treated with myriocin (intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg body weight). Further experiments revealed that the MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase) inhibitor PD98059 potently inhibited ERK phosphorylation, as expected, and increased primary hepatocyte apoA-I production by 3-fold. These results indicate that ERK phosphorylation plays a role in regulating hepatic apoA-I expression and suggest that the anti-atherogenic mechanism of action for myriocin may be linked to this pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Ballantyne C. M., Herd J. A., Dunn J. K., Jones P. H., Farmer J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Effects of lipid lowering therapy on progression of coronary and carotid artery disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1997;8:354–361. - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne C. M. Rationale for targeting multiple lipid pathways for optimal cardiovascular risk reduction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005;96:14K–19K. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S. Sphingolipids in atherosclerosis and vascular biology. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998;18:1523–1533. - PubMed
-
- Auge N., Negre-Salvayre A., Salvayre R., Levade T. Sphingomyelin metabolites in vascular cell signaling and atherogenesis. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2000;39:207–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

