HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway
- PMID: 20102415
- PMCID: PMC2842504
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03160.x
HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway
Abstract
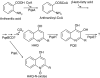
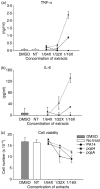
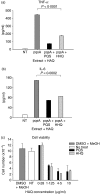
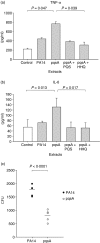
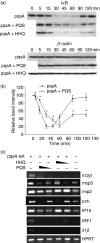
To explore whether bacterial secreted 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) can regulate host innate immune responses, we used the extracts of bacterial culture supernatants from a wild-type (PA14) and two mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that have defects in making HAQs. Surprisingly, the extract of supernatants from the P. aeruginosa pqsA mutant that does not make HAQs showed strong stimulating activity for the production of innate cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in the J774A.1 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, whereas the extract from the wild-type did not. The addition of 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ) or 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal) to mammalian cell culture media abolished this stimulating activity of the extracts of supernatants from the pqsA mutant on the expression of innate cytokines in J774A.1 cells and in the primary bronchoalveolar lavage cells from C57BL/6 mice, suggesting that HHQ and PQS can suppress the host innate immune responses. The pqsA mutant showed reduced dissemination in the lung tissue compared with the wild-type strain in a mouse in vivo intranasal infection model, suggesting that HHQ and PQS may play a role in the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa. HHQ and PQS reduced the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) binding to its binding sites and the expression of NF-kappaB target genes, and PQS delayed inhibitor of kappaB degradation, indicating that the effect of HHQ and PQS was mediated through the NF-kappaB pathway. Our results suggest that HHQ and PQS produced by P. aeruginosa actively suppress host innate immune responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global gene expression analysis on the target genes of PQS and HHQ in J774A.1 monocyte/macrophage cells.Microb Pathog. 2010 Oct;49(4):174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2010.05.009. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Microb Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20595074
-
Pseudomonas quinolone signalling system: a component of quorum sensing cascade is a crucial player in the acute urinary tract infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Nov;304(8):1199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.08.013. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25240873
-
Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 3;101(5):1339-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307694100. Epub 2004 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14739337 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Pyochelin and Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Direction for Future Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 7;25(16):8611. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168611. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting quinolone biosynthesis of Burkholderia.Chem Sci. 2021 Mar 26;12(20):6908-6912. doi: 10.1039/d0sc06167k. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34123319 Free PMC article.
-
Autolysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Mutant Is Suppressed by Staphylococcus aureus through Iron-Dependent Metabolism.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 28;34(4):795-803. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2312.12028. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38303126 Free PMC article.
-
How Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hijack the Host Immune Response in the Context of Cystic Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 1;24(7):6609. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076609. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of a 1-Cys peroxiredoxin in bacterial virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Oct 16;10(10):e1004442. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004442. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25329795 Free PMC article.
-
Interference With Quorum-Sensing Signal Biosynthesis as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Feb 5;8:444. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00444. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30805311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhavsar AP, Guttman JA, Finlay BB. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature. 2007;449:827–34. - PubMed
-
- Rello J, Diaz E. Pneumonia in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:2544–51. - PubMed
-
- Chastre J, Fagon JY. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:867–903. - PubMed
-
- Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M. The role of quorum sensing in the pathogenicity of the cunning aggressor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387:409–14. - PubMed
-
- Rumbaugh KP, Griswold JA, Hamood AN. The role of quorum sensing in the in vivo virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:1721–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

