HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway
- PMID: 20102415
- PMCID: PMC2842504
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03160.x
HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway
Abstract
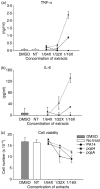
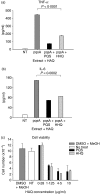
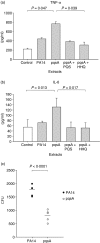
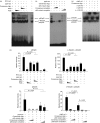
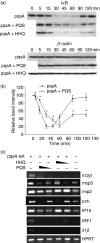
To explore whether bacterial secreted 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) can regulate host innate immune responses, we used the extracts of bacterial culture supernatants from a wild-type (PA14) and two mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that have defects in making HAQs. Surprisingly, the extract of supernatants from the P. aeruginosa pqsA mutant that does not make HAQs showed strong stimulating activity for the production of innate cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in the J774A.1 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, whereas the extract from the wild-type did not. The addition of 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ) or 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal) to mammalian cell culture media abolished this stimulating activity of the extracts of supernatants from the pqsA mutant on the expression of innate cytokines in J774A.1 cells and in the primary bronchoalveolar lavage cells from C57BL/6 mice, suggesting that HHQ and PQS can suppress the host innate immune responses. The pqsA mutant showed reduced dissemination in the lung tissue compared with the wild-type strain in a mouse in vivo intranasal infection model, suggesting that HHQ and PQS may play a role in the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa. HHQ and PQS reduced the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) binding to its binding sites and the expression of NF-kappaB target genes, and PQS delayed inhibitor of kappaB degradation, indicating that the effect of HHQ and PQS was mediated through the NF-kappaB pathway. Our results suggest that HHQ and PQS produced by P. aeruginosa actively suppress host innate immune responses.
Figures
References
-
- Bhavsar AP, Guttman JA, Finlay BB. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature. 2007;449:827–34. - PubMed
-
- Rello J, Diaz E. Pneumonia in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:2544–51. - PubMed
-
- Chastre J, Fagon JY. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:867–903. - PubMed
-
- Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M. The role of quorum sensing in the pathogenicity of the cunning aggressor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387:409–14. - PubMed
-
- Rumbaugh KP, Griswold JA, Hamood AN. The role of quorum sensing in the in vivo virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:1721–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

