Correlation between ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase and three replication proteins in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20102606
- PMCID: PMC2826317
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-11
Correlation between ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase and three replication proteins in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background: There has long been evidence supporting the idea that RNR and the dNTP-synthesizing complex must be closely linked to the replication complex or replisome. We contributed to this body of evidence in proposing the hypothesis of the replication hyperstructure. A recently published work called this postulate into question, reporting that NrdB is evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm. Consequently we were interested in the localization of RNR protein and its relationship with other replication proteins.
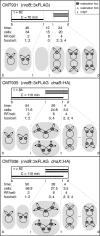
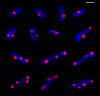
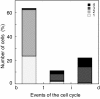
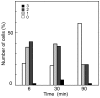
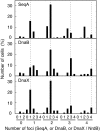
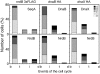
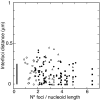
Results: We tagged NrdB protein with 3xFLAG epitope and detected its subcellular location by immunofluorescence microscopy. We found that this protein is located in nucleoid-associated clusters, that the number of foci correlates with the number of replication forks at any cell age, and that after the replication process ends the number of cells containing NrdB foci decreases.We show that the number of NrdB foci is very similar to the number of SeqA, DnaB, and DnaX foci, both in the whole culture and in different cell cycle periods. In addition, interfoci distances between NrdB and three replication proteins are similar to the distances between two replication protein foci.
Conclusions: NrdB is present in nucleoid-associated clusters during the replication period. These clusters disappear after replication ends. The number of these clusters is closely related to the number of replication forks and the number of three replication protein clusters in any cell cycle period. Therefore we conclude that NrdB protein, and most likely RNR protein, is closely linked to the replication proteins or replisome at the replication fork. These results clearly support the replication hyperstructure model.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

