Mental illness and well-being: the central importance of positive psychology and recovery approaches
- PMID: 20102609
- PMCID: PMC2835700
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-10-26
Mental illness and well-being: the central importance of positive psychology and recovery approaches
Abstract
Background: A new evidence base is emerging, which focuses on well-being. This makes it possible for health services to orientate around promoting well-being as well as treating illness, and so to make a reality of the long-standing rhetoric that health is more than the absence of illness. The aim of this paper is to support the re-orientation of health services around promoting well-being. Mental health services are used as an example to illustrate the new knowledge skills which will be needed by health professionals.
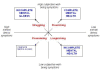
Discussion: New forms of evidence give a triangulated understanding about the promotion of well-being in mental health services. The academic discipline of positive psychology is developing evidence-based interventions to improve well-being. This complements the results emerging from synthesising narratives about recovery from mental illness, which provide ecologically valid insights into the processes by which people experiencing mental illness can develop a purposeful and meaningful life. The implications for health professionals are explored. In relation to working with individuals, more emphasis on the person's own goals and strengths will be needed, with integration of interventions which promote well-being into routine clinical practice. In addition, a more societally-focussed role for professionals is envisaged, in which a central part of the job is to influence local and national policies and practices that impact on well-being.
Summary: If health services are to give primacy to increasing well-being, rather than to treating illness, then health workers need new approaches to working with individuals. For mental health services, this will involve the incorporation of emerging knowledge from recovery and from positive psychology into education and training for all mental health professionals, and changes to some long-established working practices.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Promoting Mental Health. Concepts, Emerging Evidence, Practice. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- Mental Health Commission of Canada. Toward recovery & well-being. Calgary: Mental Health Commission of Canada, Calgary; 2009.
-
- Department of Health. New Horizons. Towards a shared vision for mental health. Consultation. London: Department of Health; 2009.
-
- Frisch MB, Cornell J, Villanueva M, Retzlaff PJ. Clinical validation of the Quality of Life Inventory: A measure of life satisfaction for use in treatment planning and outcome assessment. Psychological Assessment. 1992;4:92–101. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.4.1.92. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical