Global screening of potential Candida albicans biofilm-related transcription factors via network comparison
- PMID: 20102611
- PMCID: PMC2842261
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-53
Global screening of potential Candida albicans biofilm-related transcription factors via network comparison
Abstract
Background: Candida albicans is a commonly encountered fungal pathogen in humans. The formation of biofilm is a major virulence factor in C. albicans pathogenesis and is related to antidrug resistance of this organism. Although many factors affecting biofilm have been analyzed, molecular mechanisms that regulate biofilm formation still await to be elucidated.
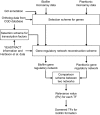
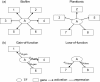
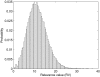
Results: In this study, from the gene regulatory network perspective, we developed an efficient computational framework, which integrates different kinds of data from genome-scale analysis, for global screening of potential transcription factors (TFs) controlling C. albicans biofilm formation. S. cerevisiae information and ortholog data were used to infer the possible TF-gene regulatory associations in C. albicans. Based on TF-gene regulatory associations and gene expression profiles, a stochastic dynamic model was employed to reconstruct the gene regulatory networks of C. albicans biofilm and planktonic cells. The two networks were then compared and a score of relevance value (RV) was proposed to determine and assign the quantity of correlation of each potential TF with biofilm formation. A total of twenty-three TFs are identified to be related to the biofilm formation; ten of them are previously reported by literature evidences.
Conclusions: The results indicate that the proposed screening method can successfully identify most known biofilm-related TFs and also identify many others that have not been previously reported. Together, this method can be employed as a pre-experiment screening approach that reveals new target genes for further characterization to understand the regulatory mechanisms in biofilm formation, which can serve as the starting point for therapeutic intervention of C. albicans infections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcription factor network efficiency in the regulation of Candida albicans biofilms: it is a small world.Curr Genet. 2018 Aug;64(4):883-888. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0804-1. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29318385
-
Systematic Complex Haploinsufficiency-Based Genetic Analysis of Candida albicans Transcription Factors: Tools and Applications to Virulence-Associated Phenotypes.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Mar 28;8(4):1299-1314. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300515. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29472308 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Mss11 in Candida albicans biofilm formation.Mol Genet Genomics. 2014 Oct;289(5):807-19. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0846-0. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Mol Genet Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24752399
-
A sticky situation: untangling the transcriptional network controlling biofilm development in Candida albicans.Transcription. 2012 Nov-Dec;3(6):315-22. doi: 10.4161/trns.22281. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Transcription. 2012. PMID: 23117819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Genetic regulatory mechanisms of Candida albicans biofilm formation].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017 Sep 25;33(9):1567-1581. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170122. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28956402 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Investigating Common Pathogenic Mechanisms between Homo sapiens and Different Strains of Candida albicans for Drug Design: Systems Biology Approach via Two-Sided NGS Data Identification.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Feb 15;11(2):119. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020119. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30769958 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Rap1 with Cell Wall Integrity, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence in Candida albicans.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0328522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03285-22. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36416583 Free PMC article.
-
A network-based biomarker approach for molecular investigation and diagnosis of lung cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2011 Jan 6;4:2. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21211025 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology as an integrated platform for bioinformatics, systems synthetic biology, and systems metabolic engineering.Cells. 2013 Oct 11;2(4):635-88. doi: 10.3390/cells2040635. Cells. 2013. PMID: 24709875 Free PMC article.
-
Essential functional modules for pathogenic and defensive mechanisms in Candida albicans infections.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:136130. doi: 10.1155/2014/136130. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24757665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d'Enfert C, Hube B. Candida: comparative and functional genomics. Wymondham: Caister Academic; 2007.
-
- Calderone RA. Candida and candidiasis. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

