Predicting emotional and social competence during early childhood from toddler risk and maternal behavior
- PMID: 20102651
- PMCID: PMC2860175
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579409990307
Predicting emotional and social competence during early childhood from toddler risk and maternal behavior
Abstract
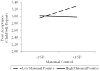
The longitudinal associations between maternal parenting behavior and toddler risk with children's emotional and social competence were examined during the transition to kindergarten, in a sample of 253 children. Toddler risk was characterized by early externalizing behavior and poor emotion regulation skills. Given that we were interested in the multiple pathways that may result in emotional and social competence, we examined the interactions among maternal parenting behavior and toddler risk. There were some significant interactions, although the pattern of results was not consistent across all competence outcomes. Maternal parenting behavior was not directly associated with children's emotional and social competence. In some instances, maternal control has differential implications for children's emotional and social competence dependent upon the child's level of early risk and maternal positive parenting. Specifically, maternal control tended to be more detrimental for children's emotional competence during the transition to kindergarten, when children exhibit higher levels of risk. Overall, it appears that there are multiple developmental pathways, depending on child and maternal characteristics that lead to early emotional and social competence.
Figures
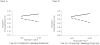
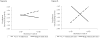
Similar articles
-
Postpartum maternal separation anxiety, overprotective parenting, and children's social-emotional well-being: longitudinal evidence from an Australian cohort.J Fam Psychol. 2013 Aug;27(4):618-28. doi: 10.1037/a0033332. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Fam Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23834364
-
Effects of early maternal distress and parenting on the development of children's self-regulation and externalizing behavior.Dev Psychopathol. 2013 May;25(2):437-53. doi: 10.1017/S0954579412001162. Dev Psychopathol. 2013. PMID: 23627955
-
Maternal depressive symptoms and child social preference during the early school years: mediation by maternal warmth and child emotion regulation.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2011 Apr;39(3):365-77. doi: 10.1007/s10802-010-9468-0. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2011. PMID: 21080053 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive effects of parenting behavior and regulatory skills in toddlerhood on child weight outcomes.Int J Obes (Lond). 2019 Jan;43(1):53-61. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0162-6. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30026591 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal emotional responsiveness and toddlers' social-emotional competence.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1993 Jul;34(5):715-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1993.tb01066.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1993. PMID: 8340440
Cited by
-
Subtypes of Aggressive Behavior in Children with Autism in the Context of Emotion Recognition, Hostile Attribution Bias, and Dysfunctional Emotion Regulation.J Autism Dev Disord. 2022 Dec;52(12):5367-5382. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05387-w. Epub 2021 Dec 20. J Autism Dev Disord. 2022. PMID: 34931277 Free PMC article.
-
Social competence and psychopathology in early childhood: a systematic review.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;28(4):443-459. doi: 10.1007/s00787-018-1152-x. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29637284
-
Intervention effects on negative affect of CPS-referred children: results of a randomized clinical trial.Child Abuse Negl. 2014 Sep;38(9):1459-67. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 10. Child Abuse Negl. 2014. PMID: 24814751 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Emotion regulation and childhood aggression: longitudinal associations.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2012 Dec;43(6):909-23. doi: 10.1007/s10578-012-0303-4. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2012. PMID: 22528031 Review.
-
Emotional Understanding, Reactivity, and Regulation in Young Children with ADHD Symptoms.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017 Oct;45(7):1297-1310. doi: 10.1007/s10802-016-0244-7. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017. PMID: 27957717
References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist/2–3 and 1992 profile. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1992.
-
- Achenbach TM, Edelbrock C. Manual for the child behavior checklist and revised child behavior profile. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1983.
-
- Achenbach TM, Edelbrock C, Howell CT. Empirically based assessment of the behavioral/emotional problems of 2- and 3-year-old children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 1987;15:629–650. - PubMed
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. London: Sage Publications; 1991.
-
- Baumrind D. The discipline controversy revisited. Family Relations. 1996;45:405–414.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

