Characterization of the six zebrafish clade B fibrillar procollagen genes, with evidence for evolutionarily conserved alternative splicing within the pro-alpha1(V) C-propeptide
- PMID: 20102740
- PMCID: PMC2862785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.01.006
Characterization of the six zebrafish clade B fibrillar procollagen genes, with evidence for evolutionarily conserved alternative splicing within the pro-alpha1(V) C-propeptide
Abstract
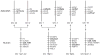
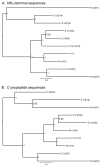
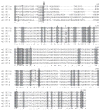
Genes for tetrapod fibrillar procollagen chains can be divided into two clades, A and B, based on sequence homologies and differences in protein domain and gene structures. Although the major fibrillar collagen types I-III comprise only clade A chains, the minor fibrillar collagen types V and XI comprise both clade A chains and the clade B chains pro-alpha1(V), pro-alpha3(V), pro-alpha1(XI) and pro-alpha2(XI), in which defects can underlie various genetic connective tissue disorders. Here we characterize the clade B procollagen chains of zebrafish. We demonstrate that in contrast to the four tetrapod clade B chains, zebrafish have six clade B chains, designated here as pro-alpha1(V), pro-alpha3(V)a and b, pro-alpha1(XI)a and b, and pro-alpha2(XI), based on synteny, sequence homologies, and features of protein domain and gene structures. Spatiotemporal expression patterns are described, as are conserved and non-conserved features that provide insights into the function and evolution of the clade B chain types. Such features include differential alternative splicing of NH(2)-terminal globular sequences and the first case of a non-triple helical imperfection in the COL1 domain of a clade B, or clade A, fibrillar procollagen chain. Evidence is also provided for previously unknown and evolutionarily conserved alternative splicing within the pro-alpha1(V) C-propeptide, which may affect selectivity of collagen type V/XI chain associations in species ranging from zebrafish to human. Data presented herein provide insights into the nature of clade B procollagen chains and should facilitate their study in the zebrafish model system.
Copyright 2010 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


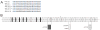


References
-
- Abedin MZ, Ayad S, Weiss JB. Isolation and native characterization of cysteine-rich collagens from bovine placental tissues and uterus and their relationship to types IV and V collagens. Biosci Rep. 1982;2:493–502. - PubMed
-
- Baas D, Malbouyres M, Haftek-Terreau Z, Le Guellec D, Ruggiero F. Craniofacial cartilage morphogenesis requires zebrafish col11a1 activity. Matrix Biol 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bernard M, Yoshioka H, Rodriguez E, Van der Rest M, Kimura T, Ninomiya Y, Olsen BR, Ramirez F. Cloning and sequencing of pro-alpha 1 (XI) collagen cDNA demonstrates that type XI belongs to the fibrillar class of collagens and reveals that the expression of the gene is not restricted to cartilagenous tissue. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:17159–66. - PubMed
-
- Birk DE, Fitch JM, Babiarz JP, Doane KJ, Linsenmayer TF. Collagen fibrillogenesis in vitro: interaction of types I and V collagen regulates fibril diameter. J Cell Sci. 1990;95(Pt 4):649–57. - PubMed
-
- Boot-Handford RP, Tuckwell DS. Fibrillar collagen: the key to vertebrate evolution? A tale of molecular incest. Bioessays. 2003;25:142–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

