Endothelial function in individuals with coronary artery disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20102776
- PMCID: PMC2891205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.12.023
Endothelial function in individuals with coronary artery disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
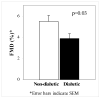
The goal of this study was to determine if individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) had greater endothelial dysfunction (ED) than individuals with only CAD. Flow-mediated dilation (FMD), calculated as percentage increase in brachial artery diameter in response to postischemic blood flow, was measured after an overnight fast in 2 cohorts. The first cohort included 76 participants in the Northern Manhattan Study with CAD; 25 also had T2DM. The second cohort was composed of 27 individuals with both T2DM and CAD who were participants in a study of postprandial lipemia. Combined, we analyzed 103 patients with CAD: 52 with T2DM (T2DM+) and 51 without T2DM (T2DM-). The 52 CAD T2DM+ subjects had a mean FMD of 3.9% +/- 3.2%, whereas the 51 CAD T2DM- subjects had a greater mean FMD of 5.5% +/- 4.0% (P < .03). An investigation of various confounders known to affect FMD identified age and body mass index as the only significant covariates in a multiple regression model. Adjusting for age and body mass index, we found that FMD remained lower in T2DM+ subjects compared with T2DM- subjects (difference, -1.99%; P < .03). In patients with CAD, the concomitant presence of T2DM is independently associated with greater ED, as measured by FMD. This finding may be relevant to the greater early and late morbidity and mortality observed in patients with both CAD and T2DM.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Severe Coronary Artery Disease: Does Diabetes Play a Contributing Role?Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 15;61(1):135. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010135. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 39859119 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive assessment of endothelial function by brachial artery flow mediated vasodilatation and its association with coronary artery disease: an Indian perspective.J Indian Med Assoc. 2004 May;102(5):243-6, 251-2. J Indian Med Assoc. 2004. PMID: 15636026
-
Endothelium-dependent brachial artery flow mediated vasodilatation in patients with diabetes mellitus with and without coronary artery disease.J Assoc Physicians India. 2003 Apr;51:355-8. J Assoc Physicians India. 2003. PMID: 12723648
-
Effects of linagliptin on endothelial function and postprandial lipids in coronary artery disease patients with early diabetes: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 May 17;17(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0716-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29773079 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Global Insights into the Impact of Endothelial Dysfunction on Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.West Afr J Med. 2024 Dec 30;41(12):1198-1204. West Afr J Med. 2024. PMID: 40392755
Cited by
-
Characterization of macro-and microvascular function and structure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;1(1):68-75. Epub 2011 May 15. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 22254187 Free PMC article.
-
The Glycocalyx and Its Role in Vascular Physiology and Vascular Related Diseases.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021 Feb;12(1):37-71. doi: 10.1007/s13239-020-00485-9. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021. PMID: 32959164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Tuning of Intrinsic Endothelial Ca2+ Dynamics in Swine Coronary Arteries.Circ Res. 2016 Apr 1;118(7):1078-90. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.308141. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 26838791 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Severe Coronary Artery Disease: Does Diabetes Play a Contributing Role?Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 15;61(1):135. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010135. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 39859119 Free PMC article.
-
Combined examination of glyceryl trinitrate-mediated vascular dilation with flow-mediated vascular dilation is essential for assessment of vascular function in type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2013 May 6;4(3):304-9. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12021. Epub 2012 Dec 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2013. PMID: 24843670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Haffner SM, et al. Elevated risk of cardiovascular disease prior to clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1129–1134. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Detection EaToHBCiA. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, et al. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with Type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–234. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg RB. Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:3171–3182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

