Coordination of molecular motors: from in vitro assays to intracellular dynamics
- PMID: 20102789
- PMCID: PMC2846361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.014
Coordination of molecular motors: from in vitro assays to intracellular dynamics
Abstract
New technologies have emerged that enable the tracking of molecular motors and their cargos with very high resolution both in vitro and in live cells. Classic in vitro motility assays are being supplemented with assays of increasing complexity that more closely model the cellular environment. In cells, the introduction of probes such as quantum dots allows the high-resolution tracking of both motors and vesicular cargos. The 'bottom up' enhancement of in vitro assays and the 'top down' analysis of motility inside cells are likely to converge over the next few years. Together, these studies are providing new insights into the coordination of motors during intracellular transport.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

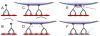
References
-
- Guerin T, Prost J, Martin P, Joanny J-F. Coordination and collective properties of molecular motors: theory. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2010 this volume. - PubMed
-
- Mallik R, Carter BC, Lex SA, King SJ, Gross SP. Cytoplasmic dynein functions as a gear in response to load. Nature. 2004;427:649–652. - PubMed
-
- Ross JL, Wallace K, Shuman H, Goldman YE, Holzbaur EL. Processive bidirectional motion of dynein-dynactin complexes in vitro. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:562–570. - PubMed
-
- Yildiz A, Forkey JN, McKinney SA, Ha T, Goldman YE, Selvin PR. Myosin V walks hand-over-hand: single fluorophore imaging with 1.5-nm localization. Science. 2003;300:2061–2065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

