Influence of diabetes mellitus on outcome in patients over 40 years of age with the long QT syndrome
- PMID: 20102896
- PMCID: PMC2813216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.08.657
Influence of diabetes mellitus on outcome in patients over 40 years of age with the long QT syndrome
Abstract
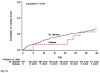
Diabetes mellitus can affect ventricular repolarization, and we investigated the impact of diabetes on the risk for cardiac events in older patients with long QT syndrome (LQTS). The study population consisted of 1,152 patients with QTc interval >/=450 ms who were enrolled in the United States portion of the International Long QT Syndrome Registry and survived >40 years of age. Patients were categorized as having diabetes if they received oral diabetic medication or insulin. End points after 40 years of age included first cardiac event (syncope, aborted cardiac arrest, sudden cardiac death, whichever occurred first) and all-cause mortality. Follow-up extended from 41 to 75 years of age. Risk factors for end points were evaluated by the Cox model. During follow-up, 193 patients had a first cardiac event, and 99 patients died. Of patients with LQTS, development of diabetes in adult patients with LQTS was not associated with an increased risk of first cardiac events dominated by syncope. Risk factors for mortality were syncope before 41 years of age, QTc interval > or =500 ms, heart rate >80 beats/min, and diabetes; there was no mortality interaction involving diabetes and QTc interval > or =500 ms. In conclusion, diabetes and prolonged QTc interval contributed independent mortality risks in adult patients with LQTS, with no interaction between these 2 risk factors.
Figures

References
-
- Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ, Crampton RS, Tzivoni D, Locati EH, MacCluer J, Hall WJ, Weitkamp L, Vincent GM, Garson A, Jr, Robinson JL, Benhorin J, Choi S. The long QT syndrome. Prospective longitudinal study of 328 families. Circulation. 1991;84:1136–1144. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg I, Moss AJ. Long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:2291–2300. - PubMed
-
- Priori SG, Schwartz PJ, Napolitano C, Bloise R, Ronchetti E, Grillo M, Vicentini A, Spazzolini C, Nastoli J, Bottelli G, Folli R, Cappelletti D. Risk stratification in the long-QT syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1866–1874. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg I, Moss AJ, Peterson DR, McNitt S, Zareba W, Andrews ML, Robinson JL, Locati EH, Ackerman MJ, Benhorin J, Kaufman ES, Napolitano C, Priori SG, Qi M, Schwartz PJ, Towbin JA, Vincent GM, Zhang L. Risk factors for aborted cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death in children with the congenital long-QT syndrome. Circulation. 2008;117:2184–2191. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hobbs JB, Peterson DR, Moss AJ, McNitt S, Zareba W, Goldenberg I, Qi M, Robinson JL, Sauer AJ, Ackerman MJ, Benhorin J, Kaufman ES, Locati EH, Napolitano C, Priori SG, Towbin JA, Vincent GM, Zhang L. Risk of aborted cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death during adolescence in the long-QT syndrome. JAMA. 2006;296:1249–1254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

