Noncanonical Wnt11 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration
- PMID: 20103596
- PMCID: PMC2824771
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0238
Noncanonical Wnt11 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration
Abstract
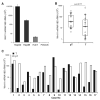
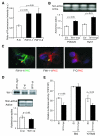
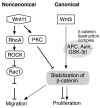
The canonical Wnt signaling is frequently activated due to overexpression and/or mutations in components of this pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the biological role of noncanonical Wnt-mediated signaling in HCC with respect to the signaling pathways involved and their physiologic function is unknown. Here, we report the role of Wnt11, a member of the noncanonical cascade, in hepatic oncogenesis. The expression levels of Wnt11 mRNA and protein were significantly downregulated in human HCC tumors compared with the adjacent uninvolved liver as measured by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR and Western blot analysis. In human HCC cell lines, overexpression of Wnt11 activated protein kinase C signaling. Protein kinase C antagonized the canonical signaling through phosphorylation of beta-catenin and reduced T-cell factor-mediated transcriptional activity, resulting in a decrease of cell proliferation. Furthermore, ectopic expression of Wnt11 promotes RhoA/Rho kinase activation. We found that activated Rho kinase inhibited Rac1 to reduce cell motility and migration. These observations suggest a novel role for Wnt11 as a tumor suppressor during hepatocarcinogenesis because loss of expression promotes the malignant phenotype via both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Canonical Wnt signaling is antagonized by noncanonical Wnt5a in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2009 Oct 22;8:90. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-90. Mol Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19849855 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of mutation and expression of beta-catenin, T-cell factor-4 and glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta genes.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003 Mar;18(3):280-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02973.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003. PMID: 12603528
-
Long noncoding RNA CASC2c inhibited cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by inactivated ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Mar;22(3):302-310. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02223-7. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31625123
-
Wnt signaling in liver cancer.Curr Drug Targets. 2008 Nov;9(11):1013-24. doi: 10.2174/138945008786786127. Curr Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18991612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Points of therapeutic intervention along the Wnt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Jul;11(6):549-59. doi: 10.2174/187152011796011019. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21554202 Review.
Cited by
-
Planar polarity: A new player in both lung development and disease.Organogenesis. 2011 Jul-Sep;7(3):209-16. doi: 10.4161/org.7.3.18462. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Organogenesis. 2011. PMID: 22030785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT ligands in non-small cell lung cancer: from pathogenesis to clinical practice.Discov Oncol. 2023 Jul 24;14(1):136. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00739-7. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37486552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of crosstalk between MAPK and Wnt signals and its impact on cartilage regeneration.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Dec;358(3):633-49. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2010-x. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 25312291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Potential Therapeutic Agents Targeting WNT/PCP Signaling.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;269:175-213. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_533. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34463852 Review.
-
Mechanism of inhibiting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma Hepa1-6 cells by embryonic stem cell-conditioned medium.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Apr;19(4):2406-2414. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8527. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32226485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laurent-Puig P, Legoix P, Bluteau O, et al. Genetic alterations associated with hepatocellular carcinomas define distinct pathways of hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1763–73. - PubMed
-
- Merle P, de la Monte S, Kim M, et al. Functional consequences of Frizzled-7 receptor overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1110–22. - PubMed
-
- Merle P, Kim M, Herrmann M, et al. Oncogenic role of the frizzled-7/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2005;43:854–62. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

