Caffeine-mediated inhibition of calcium release channel inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subtype 3 blocks glioblastoma invasion and extends survival
- PMID: 20103623
- PMCID: PMC3273964
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2886
Caffeine-mediated inhibition of calcium release channel inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subtype 3 blocks glioblastoma invasion and extends survival
Abstract
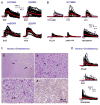
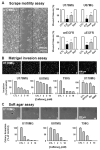
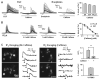
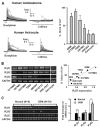
Calcium signaling is important in many signaling processes in cancer cell proliferation and motility including in deadly glioblastomas of the brain that aggressively invade neighboring tissue. We hypothesized that disturbing Ca(2+) signaling pathways might decrease the invasive behavior of giloblastoma, extending survival. Evaluating a panel of small-molecule modulators of Ca(2+) signaling, we identified caffeine as an inhibitor of glioblastoma cell motility. Caffeine, which is known to activate ryanodine receptors, paradoxically inhibits Ca(2+) increase by inositol 1,4,5-trisphospate receptor subtype 3 (IP(3)R3), the expression of which is increased in glioblastoma cells. Consequently, by inhibiting IP(3)R3-mediated Ca(2+) release, caffeine inhibited migration of glioblastoma cells in various in vitro assays. Consistent with these effects, caffeine greatly increased mean survival in a mouse xenograft model of glioblastoma. These findings suggest IP(3)R3 as a novel therapeutic target and identify caffeine as a possible adjunct therapy to slow invasive growth of glioblastoma.
Figures

References
-
- Rao JS. Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Schafer B, Gschwind A, Ullrich A. Multiple G-protein-coupled receptor signals converge on the epidermal growth factor receptor to promote migration and invasion. Oncogene. 2004;23:991–9. - PubMed
-
- Junge CE, Lee CJ, Hubbard KB, et al. Protease-activated receptor-1 in human brain: localization and functional expression in astrocytes. Exp Neurol. 2004;188:94–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

