Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status
- PMID: 20103665
- PMCID: PMC2818631
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1324
Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status
Abstract
Purpose: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family members (e.g., EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4) are commonly overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. We investigated the effects of inhibition of EGFR/HER2 signaling on pancreatic cancer to elucidate the role(s) of EGFR/HER2 in radiosensitization and to provide evidence in support of further clinical investigations.
Experimental design: Expression of EGFR family members in pancreatic cancer lines was assessed by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Cell growth inhibition was determined by MTS assay. The effects of inhibition of EGFR family receptors and downstream signaling pathways on in vitro radiosensitivity were evaluated using clonogenic assays. Growth delay was used to evaluate the effects of nelfinavir on in vivo tumor radiosensitivity.
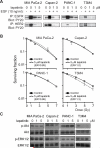
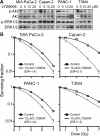
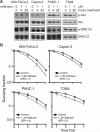
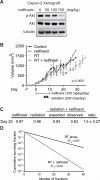
Results: Lapatinib inhibited cell growth in four pancreatic cancer cell lines, but radiosensitized only wild-type K-ras-expressing T3M4 cells. Akt activation was blocked in a wild-type K-ras cell line, whereas constitutive phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was seen in lines expressing mutant K-ras. Overexpression of constitutively active K-ras (G12V) abrogated lapatinib-mediated inhibition of both Akt phosphorylation and radiosensitization. Inhibition of MAP/ERK kinase/ERK signaling with U0126 had no effect on radiosensitization, whereas inhibition of activated Akt with LY294002 (enhancement ratio, 1.2-1.8) or nelfinavir (enhancement ratio, 1.2-1.4) radiosensitized cells regardless of K-ras mutation status. Oral nelfinavir administration to mice bearing mutant K-ras-containing Capan-2 xenografts resulted in a greater than additive increase in radiation-mediated tumor growth delay (synergy assessment ratio of 1.5).
Conclusions: Inhibition of EGFR/HER2 enhances radiosensitivity in wild-type K-ras pancreatic cancer. Nelfinavir, and other phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt inhibitors, are effective pancreatic radiosensitizers regardless of K-ras mutation status.
Figures
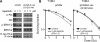
Similar articles
-
In pancreatic carcinoma, dual EGFR/HER2 targeting with cetuximab/trastuzumab is more effective than treatment with trastuzumab/erlotinib or lapatinib alone: implication of receptors' down-regulation and dimers' disruption.Neoplasia. 2012 Feb;14(2):121-30. doi: 10.1593/neo.111602. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 22431920 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the EGFR/HER2 kinase inhibitor GW572016 on EGFR- and HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell line proliferation, radiosensitization, and resistance.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Feb 1;58(2):344-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.046. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14751502
-
Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor-associated signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells: implication in radiation response.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Jul;8(7):1027-36. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0507. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20587532
-
Signaling inhibition with radiation in colorectal cancer: clinical trials.Semin Oncol. 2003 Jun;30(3 Suppl 6):56-67. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(03)00126-x. Semin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12802796 Review.
-
The EGFR-HER2 module: a stem cell approach to understanding a prime target and driver of solid tumors.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 9;35(23):2949-60. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.372. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26434585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Afatinib, an Irreversible EGFR Family Inhibitor, Shows Activity Toward Pancreatic Cancer Cells, Alone and in Combination with Radiotherapy, Independent of KRAS Status.Target Oncol. 2016 Jun;11(3):371-81. doi: 10.1007/s11523-015-0403-8. Target Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26668065
-
Upregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor 4 in oral leukoplakia.Int J Oral Sci. 2013 Mar;5(1):14-20. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2013.10. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Int J Oral Sci. 2013. PMID: 23492901 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress and their potential applications in radiotherapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 May;49(5):65. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5121. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35293589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Repurposing, an Attractive Strategy in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: Preclinical and Clinical Updates.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 5;13(16):3946. doi: 10.3390/cancers13163946. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unbiased analysis of pancreatic cancer radiation resistance reveals cholesterol biosynthesis as a novel target for radiosensitisation.Br J Cancer. 2014 Sep 9;111(6):1139-49. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.385. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25025965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts and Figures 2007. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2007.
-
- Harari PM, Huang SM. Radiation response modification following molecular inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2001;11:281–9. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–6. - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Kobrin MS, Buchler M, Beger HG, Korc M. Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with enhanced tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Res. 1993;13:565–9. - PubMed
-
- Dong M, Nio Y, Guo KJ, Tamura K, Tian YL, Dong YT. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor as prognostic indicators in Chinese patients with pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 1998;18:4613–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

