Clinical and translational studies of a phase II trial of the novel oral Akt inhibitor perifosine in relapsed or relapsed/refractory Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
- PMID: 20103671
- PMCID: PMC2885252
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1837
Clinical and translational studies of a phase II trial of the novel oral Akt inhibitor perifosine in relapsed or relapsed/refractory Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Abstract
Background: Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM) is a rare, low-grade lymphoproliferative disorder. Based on preclinical studies, we conducted a phase II clinical trial testing the efficacy and safety of the Akt inhibitor perifosine in patients with relapsed/refractory WM.
Patients and methods: Thirty-seven patients were treated with oral perifosine (150 mg daily) for six cycles. Stable or responding patients were allowed to continue therapy until progression.
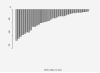
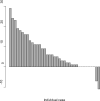
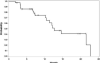
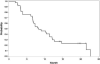
Results: The median age was 65 years (range, 44-82). The median number of prior therapy lines was two (range, one to five). Of the 37 patients, 4 achieved partial response (11%), 9 minimal response (24%), and 20 showed stable disease (54%). The median progression-free survival was 12.6 months. Additionally, beta2 microglobulin of >3.5 mg/dL was associated with poor event-free survival (P = 0.002). Perifosine was generally well tolerated; adverse events related to therapy were cytopenias (grade 3-4, 13%), gastrointestinal symptoms (grade 1-2, 81%), and arthritis flare (all grades, 11%). Translational studies using gene expression profiling and immunohistochemistry showed that perifosine inhibited pGSK activity downstream of Akt, and inhibited nuclear factor kappaB activity.
Conclusion: Perifosine resulted in at least a minimal response in 35% of patients and a median progression-free survival of 12.6 months in patients with relapsed or relapsed/refractory WM, as well as in vivo inhibition of pGSK activity. The results of this study warrant further evaluation of perifosine in combination with rituximab or other active agents in patients with WM.
Figures



References
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Panayiotidis P, Moulopoulos LA, et al. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: clinical features, complications, and management. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:214–6. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Kyle RA, Anagnostopoulos A, Treon SP. Diagnosis and management of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1564–1577. - PubMed
-
- Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, Fonseca R, Greipp PR, McMaster ML, Morra E, Pangalis GA, San Miguel JF, Branagan AR, Dimopoulos MA. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:110–115. - PubMed
-
- Ghobrial IM, Gertz MA, Fonseca R. Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:679–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

