Cyclin D2 is essential for the compensatory beta-cell hyperplastic response to insulin resistance in rodents
- PMID: 20103709
- PMCID: PMC2844846
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0838
Cyclin D2 is essential for the compensatory beta-cell hyperplastic response to insulin resistance in rodents
Abstract
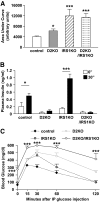
Objective: A major determinant of the progression from insulin resistance to the development of overt type 2 diabetes is a failure to mount an appropriate compensatory beta-cell hyperplastic response to maintain normoglycemia. We undertook the present study to directly explore the significance of the cell cycle protein cyclin D2 in the expansion of beta-cell mass in two different models of insulin resistance.
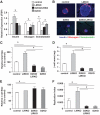
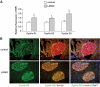
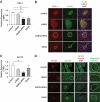
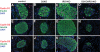
Research design and methods: We created compound knockouts by crossing mice deficient in cyclin D2 (D2KO) with either the insulin receptor substrate 1 knockout (IRS1KO) mice or the insulin receptor liver-specific knockout mice (LIRKO), neither of which develops overt diabetes on its own because of robust compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. We phenotyped the double knockouts and used RT-qPCR and immunohistochemistry to examine beta-cell mass.
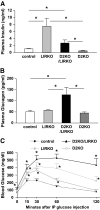
Results: Both compound knockouts, D2KO/LIRKO and D2KO/IRS1KO, exhibited insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia and an absence of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. However, the diabetic D2KO/LIRKO group rapidly succumbed early compared with a relatively normal lifespan in the glucose-intolerant D2KO/IRS1KO mice.
Conclusions: This study provides direct genetic evidence that cyclin D2 is essential for the expansion of beta-cell mass in response to a spectrum of insulin resistance and points to the cell-cycle protein as a potential therapeutic target that can be harnessed for preventing and curing type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PKCζ Is Essential for Pancreatic β-Cell Replication During Insulin Resistance by Regulating mTOR and Cyclin-D2.Diabetes. 2016 May;65(5):1283-96. doi: 10.2337/db15-1398. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26868297 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-Cell hyperplasia induced by hepatic insulin resistance: role of a liver-pancreas endocrine axis through insulin receptor A isoform.Diabetes. 2009 Apr;58(4):820-8. doi: 10.2337/db08-0551. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19136656 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin receptors in beta-cells are critical for islet compensatory growth response to insulin resistance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 22;104(21):8977-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608703104. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17416680 Free PMC article.
-
[Achievements in molecular genetics studies of diabetes mellitus].Biomed Khim. 2005 Mar-Apr;51(2):107-17. Biomed Khim. 2005. PMID: 15945346 Review. Russian.
-
Animal models of type 2 diabetes with reduced pancreatic beta-cell mass.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):873-93. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.09.007. Epub 2005 Oct 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16253543 Review.
Cited by
-
Human β-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling: driving in the dark without a road map.Diabetes. 2012 Sep;61(9):2205-13. doi: 10.2337/db12-0018. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22751699 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive β-cell proliferation increases early in high-fat feeding in mice, concurrent with metabolic changes, with induction of islet cyclin D2 expression.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jul 1;305(1):E149-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00040.2013. Epub 2013 May 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23673159 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained expression of the transcription factor GLIS3 is required for normal beta cell function in adults.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Jan;5(1):92-104. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201398. Epub 2012 Nov 29. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23197416 Free PMC article.
-
Monogenic Diabetes: What It Teaches Us on the Common Forms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes.Endocr Rev. 2016 Jun;37(3):190-222. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1116. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Endocr Rev. 2016. PMID: 27035557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKCζ Is Essential for Pancreatic β-Cell Replication During Insulin Resistance by Regulating mTOR and Cyclin-D2.Diabetes. 2016 May;65(5):1283-96. doi: 10.2337/db15-1398. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26868297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC: β-Cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003; 52: 102– 110 - PubMed
-
- Kloppel G, Lohr M, Habich K, Oberholzer M, Heitz PU: Islet pathology and the pathogenesis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus revisited. Surv Synth Pathol Res 1985; 4: 110– 125 - PubMed
-
- Ritzel RA, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Veldhuis JD, Butler PC: Relationship between β-cell mass and fasting blood glucose concentration in humans. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 717– 718 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

