Antidepressant medication and executive dysfunction: a deleterious interaction in late-life depression
- PMID: 20104069
- PMCID: PMC2818813
- DOI: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181c796d2
Antidepressant medication and executive dysfunction: a deleterious interaction in late-life depression
Abstract
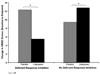
Objectives: To determine whether there is differential response to placebo or citalopram among older patients with and without deficient response inhibition (DRI).
Design: This is an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Outpatient psychiatry.
Participants: Unipolar depressed patients aged 75 years and older.
Intervention: Citalopram (20-40 mg/day) or placebo pill.
Measurements: Baseline Stroop Color-Word Test and weekly 24-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression assessments.
Results: Citalopram-treated patients with DRI did significantly worse than placebo-treated patients with DRI. Conversely, citalopram-treated patients without DRI did significantly better than placebo-treated patients without DRI.
Conclusion: Patients with late-life depression and DRI respond worse to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) than placebo. These findings suggest that there may be a deleterious interaction between DRI and antidepressant medication in late-life depression and that the mechanism of SSRI and placebo response is different.
Figures
References
-
- Podell K, Lovell MR. Neuropsychological assessment. In: Coffey CE, Cummings JL, editors. Textbook of Geriatric Neuropsychiatry. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press; 2000.
-
- Alexopoulos G, Kiosses DN, Heo M, Murphy CF, Shanmugham B, Gunning-Dixon F. Executive dysfunction and the course of geriatric depression. Biological Psychiatry. 2005;58:204–210. - PubMed
-
- Kalayam B, Alexopoulos GS. Prefrontal dysfunction and treatment response in geriatric depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1999;56(8):713–718. - PubMed
-
- Murphy GF, Alexopoulos GS. Attention network dysfunction and treatment of response of geriatric depression. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 2006;28:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Sneed JR, Roose SP, Keilp JG, Krishnan KRR, Alexopoulos GS, Sackeim HA. Response inhibition predicts poor antidepressant treatment response in very old depressed patients. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2007;15:553–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical