Retinol supplements antiviral action of interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a prospective pilot study
- PMID: 20104263
- PMCID: PMC2803131
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.09-48
Retinol supplements antiviral action of interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a prospective pilot study
Abstract
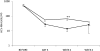
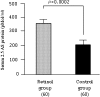
Sustained virologic response with peg-interferon and ribavirin combination therapy for 48 weeks is still inadequate. Our study examined whether short-term administration of retinol clinically influences the anti-viral activity of interferon early during interferon and ribavirin combination therapy. The control group received 6 MIU of interferon alpha-2b every day for two weeks and then 3 times a week for 22 weeks intramuscularly plus 600 mg or 800 mg per day of ribavirin orally for 24 weeks. The retinol group, in addition to above treatment, received retinol 30,000 units per day orally for 3 weeks from one week before the start of interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy. The hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA negativity rate at 1 week after the end of interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin combination therapy was 46.7% (28/60) for the retinol group and 31.7% (19/60) for the control group, which was significantly higher for the retinol group. The level of serum HCV RNA in the retinol group was significantly lower at 1 week after beginning treatment as compared to the control group (p<0.01). Furthermore, serum 2,5'AS protein at 1 week after beginning treatment was significantly higher in the retinol group (p = 0.0002). The results suggest that retinol supplement increases the antiviral effect of interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin only during the administration of IFN alpha-2b, ribavirin and retinol in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Keywords: chronic hepatitis; hepatitis C; retinol; ribavirin; virological response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon-alpha-2b plus ribavirin: a review of its use in the management of chronic hepatitis C.Drugs. 2002;62(3):507-56. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262030-00009. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11827565 Review.
-
Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of interferon alpha-2b with and without ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. The Swedish Study Group.Lancet. 1998 Jan 10;351(9096):83-7. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(97)06088-1. Lancet. 1998. PMID: 9439491 Clinical Trial.
-
Triple combination of interferon alpha-2b, ribavirin, and amantadine for treatment of chronic hepatitis C.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003 May-Jun;36(5):427-30. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200305000-00014. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12702987
-
Pegylated interferon alpha-2b (Peg-IFN alpha-2b) affects early virologic response dose-dependently in patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 during treatment with Peg-IFN alpha-2b plus ribavirin.J Viral Hepat. 2009 Aug;16(8):578-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01116.x. Epub 2009 Jun 22. J Viral Hepat. 2009. PMID: 19552663
-
Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial.Lancet. 2001 Sep 22;358(9286):958-65. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(01)06102-5. Lancet. 2001. PMID: 11583749 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A mass spectrometric analysis of 4-hydroxy-2-(E)-nonenal modification of cytochrome c.J Mass Spectrom. 2011 Mar;46(3):290-7. doi: 10.1002/jms.1890. J Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21394845 Free PMC article.
-
Might Routine Vitamin A Monitoring in Cystic Fibrosis Patients Reduce Virus-Mediated Lung Pathology?Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 9;12:704391. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.704391. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg T., von Wagner M., Nasser S., Sarrazin C., Heintges T., Gerlach T., Buggisch P., Goeser T., Rasenack J., Pape G.R., Schmidt W.E., Kallinowski B., Klinker H., Spengler U., Martus P., Alshuth U., Zeuzem S. Extended treatment duration for hepatitis C virus type 1: comparing 48 versus 72 weeks of peginterferon-alfa-2a plus ribavirin. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1086–1097. - PubMed
-
- Taliani G., Gemignani G., Ferrari C., Aceti A., Bartolozzi D., Blanc P.L., Capanni M., Esperti F., Forte P., Guadaqnino V., Mari T., Marino N., Milani S., Pasquazzi C., Rosina F., Tacconi D., Toti M., Ziqnego A.L., Messerini L., Stroffolini T. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in the retreatment of interferon-ribavirin nonresponder patients. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1098–1106. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson I.M., Gonzalez S.A., Ahmed F., Lebovics E., Min A.D., Bodenheimer H.C. Jr., Esposito S.P., Brown R.S. Jr., Brau N., Klion F.M., Tobias H., Bini E.J., Brodsky N., Cerulli M.A., Aytaman A., Gardner P.W., Geders J.M., Spivack J.E., Rahmin M.G., Berman D.H., Ehrlich J., Russo M.W., Chait M., Rovner D., Edlin B.R. A randomized trial of pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in the retreatment of chronic hepatitis C. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005;100:2453–2462. - PubMed
-
- Huber M., Weber R., Oppliger R., Vernazza P., Schmid P., Schonbucher P., Bertisch B., Meili D., Renner E.L. Interferon alpha-2a Plus Ribavirin 1,000/1,200 mg versus Interferon alpha-2a Plus Ribavirin 600 mg for Chronic Hepatitis C Infection in Patients on Opiate Maintenance Treat. Infection. 2005;33:25–29. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl K., Stahle L., Bruchfeld A., Schvarcz R. High-dose ribavirin in combination with standard dose peginterferon for treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005;41:234–236. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

