Adverse reactions to blood donations: the READ project
- PMID: 20104279
- PMCID: PMC2809512
- DOI: 10.2450/2009.0089-09
Adverse reactions to blood donations: the READ project
Abstract
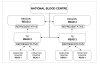
Background: In 2006 in Italy 2,404,267 donations of blood components were made by 1,539,454 donors; approximately 55% of the donations were collected directly by Transfusion Structures (TS), while about 45% were collected in Donation Centres managed by Associations and Federations of Donors. The aim of the READ (Rilevamento Eventi Avversi alla Donazione) project is to create a network of TS to test a standardised system for monitoring adverse events (AE) related to blood donations.
Materials and methods: Shared, standardised data collection forms, compatible with the forms produced by the ISBT-EHN, were prepared. Two types of form were used: (i) a form to collect data on single events (READ 1), to be used at the individual collection sites; (ii) a form for processing the data collected by each TS (READ 2).
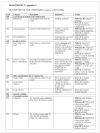
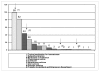
Results: Between February and August 2008 six TS collected data related to the donation of 89,332 units of blood. Overall, 523 AE were recorded. The AE occurred in 0.59% of the donations. The mean duration of the symptoms was 17 minutes. Fifteen percent of the symptoms were related to the venipuncture (mainly haematomas) and 77% to vasovagal AE. The AE were defined severe (grade C) in 47 cases. The donations in which AE were recorded were completed in 81% of the cases; 59% of the AE did not require treatment. Three donors were monitored briefly (for less than 4 hours) in hospital.
Conclusions: The use of standardised forms enabled the collection of data that could be analysed. Some problems related to the performance of the haemovigilance programme did, however, emerge: (i) organisational problems, (ii) limited sensitivity, (iii) inadequate training, and (iv) poorly defined responsibilities. These problems must be resolved at various levels: local, regional and national.
Keywords: Italian multicentre study; adverse events to donation; blood donation.
Figures






References
-
- Facco G. Haemovigilance at regional level: the experience of the region of Piedmont. Blood Transfus. 2009;7(Suppl 1):LE04.
-
- Council of Europe, January 2007: Guide to the preparation, use and quality assurance of blood components. 13^ eds, Recommendation n° R(95) 15.
-
- Catalano L, Abbonizio F, Giampaolo A, et al. Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Registro Nazionale e Regionale del Sangue e del Plasma, rapporto 2006, Rapporti ISTISAN 07/46.
-
- Fagiani P, Abraha TH, Cirillo D, et al. La sicurezza del donatore: prevenzione e assistenza dei malesseri, ABS081, XXXVIII Convegno Nazionale di Studi di Medicina Trasfusionale. Blood Transfus. 2008;6(Suppl. 1):S111–2.
-
- Misso S, Feola B, Nasti F, et al. Analisi degli eventi avversi nei donatori di sangue intero, ABS289, XXXVIII Convegno Nazionale di Studi di Medicina Trasfusionale. Blood Transfus. 2008;6(Suppl. 1):S103–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
