A biologically inspired model for pattern recognition
- PMID: 20104646
- PMCID: PMC2816315
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0910427
A biologically inspired model for pattern recognition
Abstract
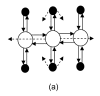
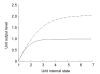
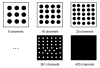
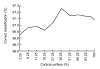
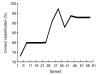
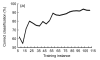
In this paper, a novel bionic model and its performance in pattern recognition are presented and discussed. The model is constructed from a bulb model and a three-layered cortical model, mimicking the main features of the olfactory system. The olfactory bulb and cortex models are connected by feedforward and feedback fibers with distributed delays. The Breast Cancer Wisconsin dataset consisting of data from 683 patients divided into benign and malignant classes is used to demonstrate the capacity of the model to learn and recognize patterns, even when these are deformed versions of the originally learned patterns. The performance of the novel model was compared with three artificial neural networks (ANNs), a back-propagation network, a support vector machine classifier, and a radial basis function classifier. All the ANNs and the olfactory bionic model were tested in a benchmark study of a standard dataset. Experimental results show that the bionic olfactory system model can learn and classify patterns based on a small training set and a few learning trials to reflect biological intelligence to some extent.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Implementing artificial neural networks through bionic construction.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 22;14(2):e0212368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212368. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30794587 Free PMC article.
-
Machine-Learning-Based Muscle Control of a 3D-Printed Bionic Arm.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 2;20(11):3144. doi: 10.3390/s20113144. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32498289 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer tumor type recognition using graph feature selection technique and radial basis function neural network with optimal structure.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Apr-Jun;14(3):625-633. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.183561. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29893330
-
A bioinspired analogous nerve towards artificial intelligence.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 14;11(1):268. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14214-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31937777 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel-distributed processing in olfactory cortex: new insights from morphological and physiological analysis of neuronal circuitry.Chem Senses. 2001 Jun;26(5):551-76. doi: 10.1093/chemse/26.5.551. Chem Senses. 2001. PMID: 11418502 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning in Human Olfactory Research.Chem Senses. 2019 Jan 1;44(1):11-22. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjy067. Chem Senses. 2019. PMID: 30371751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of Prefrontal Cortex Activity Based on Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Data upon Olfactory Stimulation.Brain Sci. 2021 May 26;11(6):701. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11060701. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073372 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

