S100A8 and S100A9 in experimental osteoarthritis
- PMID: 20105291
- PMCID: PMC2875644
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2917
S100A8 and S100A9 in experimental osteoarthritis
Abstract
Introduction: The objective was to evaluate the changes in S100A8 S100A9, and their complex (S100A8/S100A9) in cartilage during the onset of osteoarthritis (OA) as opposed to inflammatory arthritis.
Methods: S100A8 and S100A9 protein localization were determined in antigen-induced inflammatory arthritis in mice, mouse femoral head cartilage explants stimulated with interleukin-1 (IL-1), and in surgically-induced OA in mice. Microarray expression profiling of all S100 proteins in cartilage was evaluated at different times after initiation of degradation in femoral head explant cultures stimulated with IL-1 and surgically-induced OA. The effect of S100A8, S100A9 or the complex on the expression of aggrecan (Acan), collagen II (Col2a1), disintegrin and metalloproteases with thrombospondin motifs (Adamts1, Adamts 4 &Adamts 5), matrix metalloproteases (Mmp1, Mmp3, Mmp13 &Mmp14) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (Timp1, Timp2 &Timp3), by primary adult ovine articular chondrocytes was determined using real time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
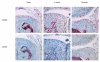
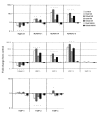
Results: Stimulation with IL-1 increased chondrocyte S100a8 and S100a9 mRNA and protein levels. There was increased chondrocyte mRNA expression of S100a8 and S100a9 in early but not late mouse OA. However, loss of the S100A8 staining in chondrocytes occurred as mouse OA progressed, in contrast to the positive reactivity for both S100A8 and S100A9 in chondrocytes in inflammatory arthritis in mice. Homodimeric S100A8 and S100A9, but not the heterodimeric complex, significantly upregulated chondrocyte Adamts1, Adamts4 and Adamts 5, Mmp1, Mmp3 and Mmp13 gene expression, while collagen II and aggrecan mRNAs were significantly decreased.
Conclusions: Chondrocyte derived S100A8 and S100A9 may have a sustained role in cartilage degradation in inflammatory arthritis. In contrast, while these proteins may have a role in initiating early cartilage degradation in OA by upregulating MMPs and aggrecanases, their reduced expression in late stages of OA suggests they do not have an ongoing role in cartilage degradation in this non-inflammatory arthropathy.
Figures




References
-
- Vogl T, Ludwig S, Goebeler M, Strey A, Thorey IS, Reichelt R, Foell D, Gerke V, Manitz MP, Nacken W, Werner S, Sorg C, Roth J. MRP8 and MRP14 control microtubule reorganization during transendothelial migration of phagocytes. Blood. 2004;104:4260–4268. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cecil DL, Johnson K, Rediske J, Lotz M, Schmidt AM, Terkeltaub R. Inflammation-induced chondrocyte hypertrophy is driven by receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Immunol. 2005;175:8296–8302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

