A review of health utilities across conditions common in paediatric and adult populations
- PMID: 20105304
- PMCID: PMC2828427
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-8-12
A review of health utilities across conditions common in paediatric and adult populations
Abstract
Background: Cost-utility analyses are commonly used in economic evaluations of interventions or conditions that have an impact on health-related quality of life. However, evaluating utilities in children presents several challenges since young children may not have the cognitive ability to complete measurement tasks and thus utility values must be estimated by proxy assessors. Another solution is to use utilities derived from an adult population. To better inform the future conduct of cost-utility analyses in paediatric populations, we reviewed the published literature reporting utilities among children and adults across selected conditions common to paediatric and adult populations.
Methods: An electronic search of Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library up to November 2008 was conducted to identify studies presenting utility values derived from the Health Utilities Index (HUI) or EuroQoL-5Dimensions (EQ-5D) questionnaires or using time trade off (TTO) or standard gamble (SG) techniques in children and/or adult populations from randomized controlled trials, comparative or non-comparative observational studies, or cross-sectional studies. The search was targeted to four chronic diseases/conditions common to both children and adults and known to have a negative impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
Results: After screening 951 citations identified from the literature search, 77 unique studies included in our review evaluated utilities in patients with asthma (n = 25), cancer (n = 23), diabetes mellitus (n = 11), skin diseases (n = 19) or chronic diseases (n = 2), with some studies evaluating multiple conditions. Utility values were estimated using HUI (n = 33), EQ-5D (n = 26), TTO (n = 12), and SG (n = 14), with some studies applying more than one technique to estimate utility values. 21% of studies evaluated utilities in children, of those the majority being in the area of oncology. No utility values for children were reported in skin diseases. Although few studies provided comparative information on utility values between children and adults, results seem to indicate that utilities may be similar in adolescents and young adults with asthma and acne. Differences in results were observed depending on methods and proxies.
Conclusions: This review highlights the need to conduct future research regarding measurement of utilities in children.
Figures
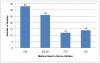
References
-
- Paediatric Quality of Life. The development of a paediatric health related quality of life measure for use in economic evaluation: The Child Health Utility 9D (CHU 9D) The University of Sheffield; 2009. http://www.shef.ac.uk/scharr/sections/heds/mvh/paediatric
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

