The mitochondria-independent cytotoxic effect of nelfinavir on leukemia cells can be enhanced by sorafenib-mediated mcl-1 downregulation and mitochondrial membrane destabilization
- PMID: 20105315
- PMCID: PMC2836985
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-19
The mitochondria-independent cytotoxic effect of nelfinavir on leukemia cells can be enhanced by sorafenib-mediated mcl-1 downregulation and mitochondrial membrane destabilization
Abstract
Background: Nelfinavir is an HIV protease inhibitor that has been used for a long period of time to treat HIV-infected individuals. It has recently emerged that nelfinavir could represent a prospective new anti-cancer drug, prompting us to test the effect of nelfinavir on leukemia cells.
Methods: By combining in vitro and ex vivo studies, the effect of nelfinavir on leukemia cells and non-malignant, bone marrow-derived tissue cells was analyzed.
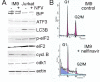
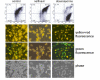
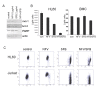
Results: At a concentration of 9 microg/ml, nelfinavir induced death of 90% of HL60, IM9, and Jurkat cells. At the same concentration and treatment conditions, less than 10% of aspirated human bone marrow cells showed nelfinavir-induced cell damage. Nelfinavir-induced death of leukemia cells was accompanied by activation of caspases 3, 7, and 8. Despite caspase activation, the upregulation of the anti-apoptotic bcl-2 family member protein mcl-1 that resulted from nelfinavir treatment stabilized the mitochondrial membrane potential, resulting in primarily mitochondria-independent cell death. Pharmacological downregulation of mcl-1 expression by treatment with sorafenib (2 microg/ml) significantly enhanced nelfinavir-induced apoptosis even at lower nelfinavir concentrations (5 microg/ml), but did not have additional detrimental effects on non-malignant bone marrow cells.
Conclusions: The ability of nelfinavir to induce apoptosis in leukemia cells as a single agent in a mitochondria-independent manner might suggest it could be used as a second or third line of treatment for leukemia patients for whom standard mitochondria-directed treatment strategies have failed. Combination treatment with nelfinavir and sorafenib might further enhance the efficacy of nelfinavir even on chemo-resistant leukemia cells.
Figures



References
-
- Gills JJ, Lopiccolo J, Tsurutani J, Shoemaker RH, Best CJ, Abu-Asab MS, Borojerdi J, Warfel NA, Gardner ER, Danish M, Hollander MC, Kawabata S, Tsokos M, Figg WD, Steeg PS, Dennis PA. Nelfinavir, A lead HIV protease inhibitor, is a broad-spectrum, anticancer agent that induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5183–5184. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0161. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Plastaras JP, Vapiwala N, Ahmed MS, Gudonis D, Cerniglia GJ, Feldman MD, Frank I, Gupta AK. Validation and toxicity of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition by HIV protease inhibitors in humans. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7:628–635. - PubMed
-
- Brunner TB, Geiger M, Grabenbauer GG, Lang-Welzenbach M, Mantoni TS, Cavallaro A, Sauer R, Hohenberger W, McKenna WG. Phase I trial of the human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor nelfinavir and chemoradiation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2699–2706. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2355. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

