Relationship between perceived body weight and body mass index based on self- reported height and weight among university students: a cross-sectional study in seven European countries
- PMID: 20105333
- PMCID: PMC2824734
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-40
Relationship between perceived body weight and body mass index based on self- reported height and weight among university students: a cross-sectional study in seven European countries
Abstract
Background: Despite low rates of obesity, many university students perceive themselves as overweight, especially women. This is of concern, because inappropriate weight perceptions can lead to unhealthy behaviours including eating disorders.
Methods: We used the database from the Cross National Student Health Survey (CNSHS), consisting of 5,900 records of university students from Bulgaria, Denmark, Germany, Lithuania, Poland, Spain and Turkey to analyse differences in perceived weight status based on the question: "Do you consider yourself much too thin, a little too thin, just right, a little too fat or much too fat?". The association between perceived weight and body mass index (BMI) calculated from self-reported weight and height was assessed with generalized non-parametric regression in R library gam.
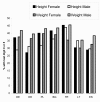
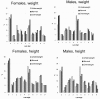
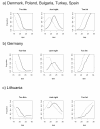
Results: Although the majority of students reported a normal BMI (72-84% of males, 65-83% of females), only 32% to 68% of students considered their weight "just right". Around 20% of females with BMI of 20 kg/m2 considered themselves "a little too fat" or "too fat", and the percentages increased to 60% for a BMI of 22.5 kg/m2. Male students rarely felt "a little too fat" or "too fat" below BMI of 22.5 kg/m2, but most felt too thin with a BMI of 20 kg/m2.
Conclusions: Weight ideals are rather uniform across the European countries, with female students being more likely to perceive themselves as "too fat" at a normal BMI, while male students being more likely to perceive themselves as "too thin". Programs to prevent unhealthy behaviours to achieve ill-advised weight ideals may benefit students.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, Regional Office for Europe. The challenge of obesity in the WHO European Region and the strategies for response. http://www.euro.who.int/document/E90711.pdf [accessed 2009 June 5]
-
- Cheung P, Ip PL, Lam ST, Bibby H. A study on body weight perception and weight control behaviours among adolescents in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med J. 2007;10:16–21. - PubMed
-
- ter Bogt TF, van Dorsselaer SA, Monshouwer K, Verdurmen JE, Engels RC, Vollebergh WA. Body mass index and body weight perception as risk factors for internalizing and externalizing problem behavior among adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2006;10:27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2005.09.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bellisle F, Monneuse MO, Steptoe A, Wardle J. Weight concerns and eating patterns: a survey of university students in Europe. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995;10:723–730. - PubMed

