Genetic studies on the functional relevance of the protein prenyltransferases in skin keratinocytes
- PMID: 20106865
- PMCID: PMC2846164
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq036
Genetic studies on the functional relevance of the protein prenyltransferases in skin keratinocytes
Abstract
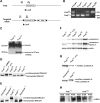
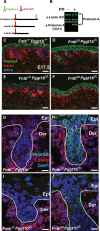
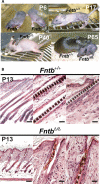
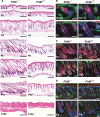
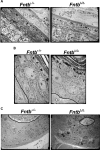
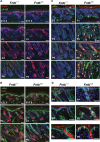
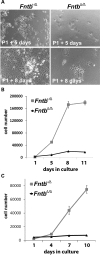
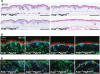
The modification of proteins with farnesyl or geranylgeranyl lipids, a process called protein prenylation, facilitates interactions of proteins with membrane surfaces. Protein prenylation is carried out by a pair of cytosolic enzymes, protein farnesyltransferase (FTase) and protein geranylgeranyltransferase type I (GGTase-I). FTase and GGTase-I have attracted interest as therapeutic targets for both cancer and progeria, but very little information exists on the importance of these enzymes for homeostasis of normal tissues. One study actually suggested that FTase is entirely dispensable. To explore the importance of the protein prenyltransferases for normal tissues, we used conditional knockout alleles for Fntb and Pggt1b (which encode the beta-subunits of FTase and GGTase-I, respectively) and a keratin 14-Cre transgene to create mice lacking FTase or GGTase-I in skin keratinocytes. Keratinocyte-specific Fntb knockout mice were viable but developed severe alopecia. Although hair follicles appeared normal during development, they were morphologically abnormal after birth, and ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies revealed many apoptotic cells. The interfollicular epidermis of Fntb-deficient mice appeared normal; however, keratinocytes from these mice could not proliferate in culture. As expected, non-farnesylated prelamin A and non-farnesylated DNAJA1 accumulated in Fntb-deficient keratinocytes. Keratinocyte-specific Pggt1b knockout mice survived development but died shortly after birth. Like Fntb-deficient keratinocytes, Pggt1b-deficient keratinocytes did not proliferate in culture. Thus, both FTase and GGTase-I are required for the homeostasis of skin keratinocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Severe hepatocellular disease in mice lacking one or both CaaX prenyltransferases.J Lipid Res. 2012 Jan;53(1):77-86. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M021220. Epub 2011 Oct 28. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22039581 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of protein farnesyltransferase to a geranylgeranyltransferase.Biochemistry. 2006 Aug 15;45(32):9746-55. doi: 10.1021/bi060295e. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16893176
-
Genetic evidence for in vivo cross-specificity of the CaaX-box protein prenyltransferases farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase-I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4260-75. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4260-4275.1993. Mol Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8321228 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Prenyltransferases and Their Inhibitors: Structural and Functional Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 12;23(10):5424. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105424. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Geranylgeranyltransferase Type 1 as a Target in Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(7):563-71. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666151203224603. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26648485 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting protein prenylation in progeria.Sci Transl Med. 2013 Feb 6;5(171):171ps3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005229. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23390246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of protein geranylgeranyltransferase-I lead to prelamin A accumulation in cells by inhibiting ZMPSTE24.J Lipid Res. 2012 Jun;53(6):1176-82. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M026161. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22448028 Free PMC article.
-
A small-molecule ICMT inhibitor delays senescence of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome cells.Elife. 2021 Feb 2;10:e63284. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63284. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33526168 Free PMC article.
-
Severe hepatocellular disease in mice lacking one or both CaaX prenyltransferases.J Lipid Res. 2012 Jan;53(1):77-86. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M021220. Epub 2011 Oct 28. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22039581 Free PMC article.
-
Tipifarnib prevents development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Mar 1;113(3):276-287. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw258. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28395021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casey P.J., Seabra M.C. Protein prenyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:5289–5292. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F.L., Casey P.J. Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:241–269. - PubMed
-
- Boyartchuk V.L., Ashby M.N., Rine J. Modulation of Ras and a-factor function by carboxyl-terminal proteolysis. Science. 1997;275:1796–1800. - PubMed
-
- Kim E., Ambroziak P., Otto J.C., Taylor B., Ashby M., Shannon K., Casey P.J., Young S.G. Disruption of the mouse Rce1 gene results in defective Ras processing and mislocalization of Ras within cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:8383–8390. - PubMed
-
- Otto J.C., Kim E., Young S.G., Casey P.J. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian prenyl protein-specific protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:8379–8382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

