Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson disease-associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central nervous system changes
- PMID: 20106867
- PMCID: PMC2850613
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq038
Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson disease-associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central nervous system changes
Abstract
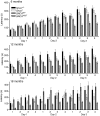
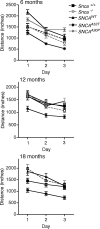
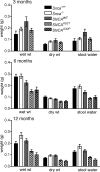
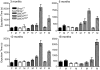
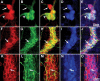
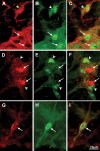
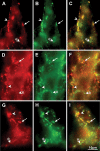
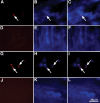
Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease with motor as well as non-motor signs in the gastrointestinal tract that include dysphagia, gastroparesis, prolonged gastrointestinal transit time, constipation and difficulty with defecation. The gastrointestinal dysfunction commonly precedes the motor symptoms by decades. Most PD is sporadic and of unknown etiology, but a fraction is familial. Among familial forms of PD, a small fraction is caused by missense (A53T, A30P and E46K) and copy number mutations in SNCA which encodes alpha-synuclein, a primary protein constituent of Lewy bodies, the pathognomonic protein aggregates found in neurons in PD. We set out to develop transgenic mice expressing mutant alpha-synuclein (either A53T or A30P) from insertions of an entire human SNCA gene as models for the familial disease. Both the A53T and A30P lines show robust abnormalities in enteric nervous system (ENS) function and synuclein-immunoreactive aggregates in ENS ganglia by 3 months of age. The A53T line also has abnormal motor behavior but neither demonstrates cardiac autonomic abnormalities, olfactory dysfunction, dopaminergic neurotransmitter deficits, Lewy body inclusions or neurodegeneration. These animals recapitulate the early gastrointestinal abnormalities seen in human PD. The animals also serve as an in vivo system in which to investigate therapies for reversing the neurological dysfunction that target alpha-synuclein toxicity at its earliest stages.
Figures
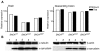
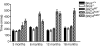
References
-
- Nussbaum R.L., Ellis C.E. Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1356–1364. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Del Tredici K., Bratzke H., Hamm-Clement J., Sandmann-Keil D., Rub U. Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson's disease (preclinical and clinical stages) J. Neurol. 2002;249(Suppl. 3):III/1–5. - PubMed
-
- Halliday G.M., Del Tredici K., Braak H. Critical appraisal of brain pathology staging related to presymptomatic and symptomatic cases of sporadic Parkinson's disease. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 2006;70:99–103. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Ghebremedhin E., Rub U., Bratzke H., Del Tredici K. Stages in the development of Parkinson's disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318:121–134. - PubMed
-
- Wolters E., Braak H. Parkinson's disease: premotor clinico-pathological correlations. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 2006:309–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

