The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in the regulation of cell-cell contact and tumor growth
- PMID: 20106901
- PMCID: PMC6276890
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgq028
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in the regulation of cell-cell contact and tumor growth
Abstract
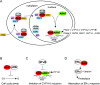
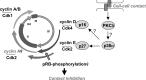
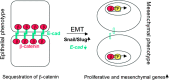
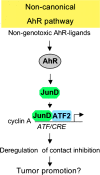
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor, which is activated by a large group of environmental pollutants including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins and planar polychlorinated biphenyls. Ligand binding leads to dimerization of the AhR with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator and transcriptional activation of several xenobiotic phase I and phase II metabolizing enzymes, such as cytochrome P4501A1 and glutathione-S-transferase, respectively. Since phase I enzymes convert inert carcinogens to active genotoxins, the AhR plays a key role in tumor initiation. Besides this classical route, the AhR mediates tumor promotion and recent evidence suggests that the AhR also plays a role in tumor progression. To date, no mechanistic link could be established between the canonical pathway involving xenobiotic metabolism and AhR-dependent tumor promotion and progression. A hallmark of tumor promotion is unbalanced proliferation, whereas tumor progression is characterized by dedifferentiation, increased motility and metastasis of tumor cells. Tumor progression and presumably also tumor promotion are triggered by loss of cell-cell contact. Cell-cell contact is known to be a critical regulator of proliferation, differentiation and cell motility in vitro and in vivo. Increasing evidence suggests that activation of the AhR may lead to deregulation of cell-cell contact, thereby inducing unbalanced proliferation, dedifferentiation and enhanced motility. In line with this is the finding of increased AhR expression and malignancy in some animal and human cancers. Here, we summarize our current knowledge on non-canonical AhR-driven pathways being involved in deregulation of cell-cell contact and discuss the data with respect to tumor initiation, promotion and progression.
Figures
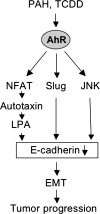
References
-
- Whitlock JP., Jr. Mechanistic aspects of dioxin action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993;6:754–763. - PubMed
-
- Hankinson O. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995;35:307–340. - PubMed
-
- Rowlands JC, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signal transduction. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1997;27:109–134. - PubMed
-
- Swanson HI, et al. The AH-receptor: genetics, structure and function. Pharmacogenetics. 1993;3:213–230. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, et al. Ligand binding and activation of the Ah receptor. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002;141:2–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

