Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling
- PMID: 20106948
- PMCID: PMC2855350
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq024
Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling
Abstract
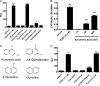
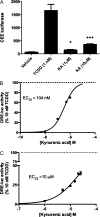
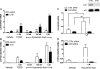
Inflammatory signaling plays a key role in tumor progression, and the pleiotropic cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an important mediator of protumorigenic properties. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) with exogenous ligands coupled with inflammatory signals can lead to synergistic induction of IL6 expression in tumor cells. Whether there are endogenous AHR ligands that can mediate IL6 production remains to be established. The indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase pathway is a tryptophan oxidation pathway that is involved in controlling immune tolerance, which also aids in tumor escape. We screened the metabolites of this pathway for their ability to activate the AHR; results revealed that kynurenic acid (KA) is an efficient agonist for the human AHR. Structure-activity studies further indicate that the carboxylic acid group is required for significant agonist activity. KA is capable of inducing CYP1A1 messenger RNA levels in HepG2 cells and inducing CYP1A-mediated metabolism in primary human hepatocytes. In a human dioxin response element-driven stable reporter cell line, the EC(25) was observed to be 104nM, while in a mouse stable reporter cell line, the EC(25) was 10muM. AHR ligand competition binding assays revealed that KA is a ligand for the AHR. Treatment of MCF-7 cells with interleukin-1beta and a physiologically relevant concentration of KA (e.g., 100nM) leads to induction of IL6 expression that is largely dependent on AHR expression. Our findings have established that KA is a potent AHR endogenous ligand that can induce IL6 production and xenobiotic metabolism in cells at physiologically relevant concentrations.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi J, Mori Y, Matsui S, Takigami H, Fujino J, Kitagawa H, Miller CA, III, Kato T, Saeki K, Matsuda T. Indirubin and indigo are potent aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands present in human urine. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:31475–31478. - PubMed
-
- Bauer TM, Jiga LP, Chuang JJ, Randazzo M, Opelz G, Terness P. Studying the immunosuppressive role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: tryptophan metabolites suppress rat allogeneic T-cell responses in vitro and in vivo. Transpl. Int. 2005;18:95–100. - PubMed
-
- Cherayil BJ. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in intestinal immunity and inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1391–1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

