Diagnosing human anisakiasis: recombinant Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 allergens versus the UniCAP 100 fluorescence enzyme immunoassay
- PMID: 20107002
- PMCID: PMC2849323
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00443-09
Diagnosing human anisakiasis: recombinant Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 allergens versus the UniCAP 100 fluorescence enzyme immunoassay
Abstract
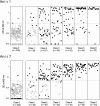
Commercially available serological methods for serodiagnosis of human anisakiasis either are poorly specific or do not include some of the most relevant Anisakis allergens. The use of selected recombinant allergens may improve serodiagnosis. To compare the diagnostic and clinical values of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods based on Ani s 1 and Ani s 7 recombinant allergens and of the UniCAP 100 fluorescence enzyme immunoassay (CAP FEIA) system, we tested sera from 495 allergic and 25 non-food-related allergic patients. The decay in specific IgE antibodies in serum was also investigated in 15 positive patients over a period of 6 to 38 months. Considering sera that tested positive by either Ani s 1 or Ani s 7 ELISA, the CAP FEIA classified 25% of sera as falsely positive, mainly in the group of patients with the lowest levels of anti-Anisakis IgE antibodies, and 1.28% of positive sera as falsely negative. Considering allergens individually, the overall sensitivities of Ani s 7 ELISA and Ani s 1 ELISA were 94% and 61%, respectively. The results also showed that anti-Anisakis IgE antibodies can be detected in serum for longer with Ani s 1 ELISA than with Ani s 7 ELISA and CAP FEIA (P < 0.01). Our findings suggest that ELISA methods with Ani s 7 and Ani s 1 allergens as targets of IgE antibodies are currently the best option for serodiagnosis of human anisakiasis, combining specificity and sensitivity. The different persistence of anti-Ani s 1 and anti-Ani s 7 antibodies in serum may help clinicians to distinguish between recent and old Anisakis infections.
Figures

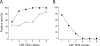
References
-
- Alonso, A., A. Moreno-Ancillo, A. Daschner, and M. C. López-Serrano. 1999. Dietary assessment in five cases of allergic reactions due to gastroallergic anisakiasis. Allergy 54:517-520. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Gómez, A., A. Moreno-Ancillo, M. C. López-Serrano, J. M. Suarez-de-Parga, A. Daschner, M. T. Caballero, P. Barranco, and R. Cabañas. 2004. Anisakis simplex only provokes allergic symptoms when the worm parasitises the gastrointestinal tract. Parasitol. Res. 93:378-384. - PubMed
-
- Audícana, M. T., L. Fernández de Corres, D. Muñoz, E. Fernández, J. A. Navarro, and M. D. del Pozo. 1995. Recurrent anaphylaxis caused by Anisakis simplex parasitizing fish. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 96:558-560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

