Development of a bead immunoassay to measure Vi polysaccharide-specific serum IgG after vaccination with the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Vi polysaccharide
- PMID: 20107010
- PMCID: PMC2837971
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00354-09
Development of a bead immunoassay to measure Vi polysaccharide-specific serum IgG after vaccination with the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Vi polysaccharide
Abstract
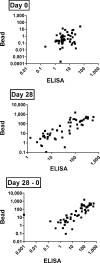
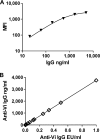
Vi polysaccharide from Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi is used as one of the available vaccines to prevent typhoid fever. Measurement of Vi-specific serum antibodies after vaccination with Vi polysaccharide by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) may be complicated due to poor binding of the Vi polysaccharide to ELISA plates resulting in poor reproducibility of measured antibody responses. We chemically conjugated Vi polysaccharide to fluorescent beads and performed studies to determine if a bead-based immunoassay provided a reproducible method to measure vaccine-induced anti-Vi serum IgG antibodies. Compared to ELISA, the Vi bead immunoassay had a lower background and therefore a greater signal-to-noise ratio. The Vi bead immunoassay was used to evaluate serum anti-Vi IgG in 996 subjects from the city of Kolkata, India, before and after vaccination. Due to the location being one where Salmonella serotype Typhi is endemic, approximately 45% of the subjects had protective levels of anti-Vi serum IgG (i.e., 1 microg/ml anti-Vi IgG) before vaccination, and nearly 98% of the subjects had protective levels of anti-Vi serum IgG after vaccination. Our results demonstrate that a bead-based immunoassay provides an effective, reproducible method to measure serum anti-Vi IgG responses before and after vaccination with the Vi polysaccharide vaccine.
Figures
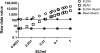

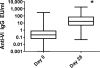
Similar articles
-
Vi Capsular Polysaccharide Produced by Recombinant Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi A Confers Immunoprotection against Infection by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Apr 24;7:135. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00135. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28484685 Free PMC article.
-
Re-examination of immune response and estimation of anti-Vi IgG protective threshold against typhoid fever-based on the efficacy trial of Vi conjugate in young children.Vaccine. 2014 Apr 25;32(20):2359-63. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.02.050. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24630869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Measurement of Typhi Vi antibodies can be used to assess adaptive immunity in patients with immunodeficiency.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Jun;192(3):292-301. doi: 10.1111/cei.13105. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29377063 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement and interpretation of Salmonella typhi Vi IgG antibodies for the assessment of adaptive immunity.J Immunol Methods. 2018 Aug;459:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2018.05.013. Epub 2018 May 22. J Immunol Methods. 2018. PMID: 29800575 Review.
-
Population impact of Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010 May;9(5):485-96. doi: 10.1586/erv.10.43. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010. PMID: 20450323 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics of immune response to typhoid and cholera vaccines.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 19;370(1671):20140142. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0142. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25964454 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of vaccine-induced antibody responses: impact of new technologies.Vaccine. 2013 Jun 7;31(25):2756-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.03.065. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23583812 Free PMC article.
-
Fifth Percentile Cutoff Values for Antipneumococcal Polysaccharide and Anti-Salmonella typhi Vi IgG Describe a Normal Polysaccharide Response.Front Immunol. 2017 May 12;8:546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00546. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28553290 Free PMC article.
-
A human IgG anti-Vi reference for Salmonella typhi with weight-based antibody units assigned.Vaccine. 2013 Apr 8;31(15):1970-4. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23422143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya, I. L., C. U. Lowe, R. Thapa, V. L. Gurubacharya, M. B. Shrestha, M. Cadoz, D. Schulz, J. Armand, D. A. Bryla, B. Trollfors, et al. 1987. Prevention of typhoid fever in Nepal with the Vi capsular polysaccharide of Salmonella typhi: a preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 317:1101. - PubMed
-
- Acosta, C. J., C. M. Galindo, R. L. Ochiai, M. C. Danovaro-Holliday, A. L. Page, V. D. Thiem, J. K. Park, E. Park, H. Koo, X. Y. Wang, R. Abu-Elyazeed, M. Ali, M. J. Albert, B. Ivanoff, T. Pang, Z. Y. Xu, and J. D. Clemens. 2004. The role of epidemiology in the introduction of vi polysaccharide typhoid fever vaccines in Asia. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 22:240-245. - PubMed
-
- Barra, A., D. Schulz, P. Aucouturier, and J. L. Preud'homme. 1988. Measurement of anti-Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies by ELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 115:111-117. - PubMed
-
- Biagini, R. E., D. L. Sammons, J. P. Smith, B. A. MacKenzie, C. A. Striley, V. Semenova, E. Steward-Clark, K. Stamey, A. E. Freeman, C. P. Quinn, and J. E. Snawder. 2004. Comparison of a multiplexed fluorescent covalent microsphere immunoassay and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measurement of human immunoglobulin G antibodies to anthrax toxins. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 11:50-55. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

