Cell type-specific long-term plasticity at glutamatergic synapses onto hippocampal interneurons expressing either parvalbumin or CB1 cannabinoid receptor
- PMID: 20107060
- PMCID: PMC2817897
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3481-09.2010
Cell type-specific long-term plasticity at glutamatergic synapses onto hippocampal interneurons expressing either parvalbumin or CB1 cannabinoid receptor
Abstract
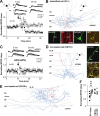
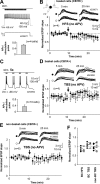
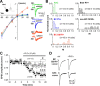
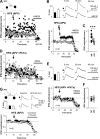
Different GABAergic interneuron types have specific roles in hippocampal function, and anatomical as well as physiological features vary greatly between interneuron classes. Long-term plasticity of interneurons has mostly been studied in unidentified GABAergic cells and is known to be very heterogeneous. Here we tested whether cell type-specific plasticity properties in distinct GABAergic interneuron types might underlie this heterogeneity. We show that long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD), two common forms of synaptic plasticity, are expressed in a highly cell type-specific manner at glutamatergic synapses onto hippocampal GABAergic neurons. Both LTP and LTD are generated in interneurons expressing parvalbumin (PV+), whereas interneurons with similar axon distributions but expressing cannabinoid receptor-1 show no lasting plasticity in response to the same protocol. In addition, LTP or LTD occurs in PV+ interneurons with different efferent target domains. Perisomatic-targeting PV+ basket and axo-axonic interneurons express LTP, whereas glutamatergic synapses onto PV+ bistratified cells display LTD. Both LTP and LTD are pathway specific, independent of NMDA receptors, and occur at synapses with calcium-permeable (CP) AMPA receptors. Plasticity in interneurons with CP-AMPA receptors strongly modulates disynaptic GABAergic transmission onto CA1 pyramidal cells. We propose that long-term plasticity adjusts the synaptic strength between pyramidal cells and interneurons in a cell type-specific manner and, in the defined CA1 interneurons, shifts the spatial pattern of inhibitory weight from pyramidal cell dendrites to the perisomatic region.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell-type specific GABA synaptic transmission and activity-dependent plasticity in rat hippocampal stratum radiatum interneurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04207.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029207
-
Calcium-permeable AMPA receptors provide a common mechanism for LTP in glutamatergic synapses of distinct hippocampal interneuron types.J Neurosci. 2012 May 9;32(19):6511-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0206-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22573673 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mechanisms of transmission at three types of mossy fiber synapse.J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 15;20(22):8279-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08279.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11069934 Free PMC article.
-
LTP and LTD in cortical GABAergic interneurons: emerging rules and roles.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Apr;60(5):712-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.020. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21185319 Review.
-
GABAergic interneurons targeting dendrites of pyramidal cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Sep;30(6):947-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06913.x. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19735288 Review.
Cited by
-
The less things change, the more they are different: contributions of long-term synaptic plasticity and homeostasis to memory.Learn Mem. 2014 Feb 14;21(3):128-34. doi: 10.1101/lm.027326.112. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24532836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic calcium nonlinearities switch the direction of synaptic plasticity in fast-spiking interneurons.J Neurosci. 2014 Mar 12;34(11):3864-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2253-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24623765 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptor subtypes mediating synaptic activation of prefrontal cortex neurons: relevance for schizophrenia.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 5;31(1):142-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1970-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21209199 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental origin dictates interneuron AMPA and NMDA receptor subunit composition and plasticity.Nat Neurosci. 2013 Aug;16(8):1032-41. doi: 10.1038/nn.3459. Epub 2013 Jul 14. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23852113 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation of the Feedforward Dentate Gyrus-CA3 Microcircuit.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016 Oct 17;8:32. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2016.00032. eCollection 2016. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27799909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali AB. Presynaptic inhibition of GABAA receptor-mediated unitary IPSPs by cannabinoid receptors at synapses between CCK-positive interneurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P. Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Bleasdale C, Dalezios Y, Somogyi P, Klausberger T. Immunoreactivity for the GABAA receptor alpha1 subunit, somatostatin and Connexin36 distinguishes axoaxonic, basket, and bistratified interneurons of the rat hippocampus. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:2094–2107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
