Quantal analysis reveals a functional correlation between presynaptic and postsynaptic efficacy in excitatory connections from rat neocortex
- PMID: 20107071
- PMCID: PMC2825095
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3244-09.2010
Quantal analysis reveals a functional correlation between presynaptic and postsynaptic efficacy in excitatory connections from rat neocortex
Abstract
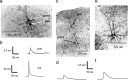
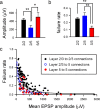
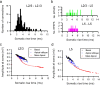
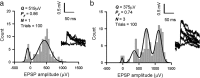
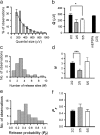
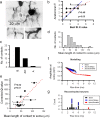
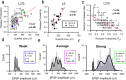
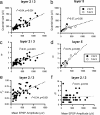
At many central synapses, the presynaptic bouton and postsynaptic density are structurally correlated. However, it is unknown whether this correlation extends to the functional properties of the synapses. To investigate this, we made recordings from synaptically coupled pairs of pyramidal neurons in rat visual cortex. The mean peak amplitude of EPSPs recorded from pairs of L2/3 neurons ranged between 40 microV and 2.9 mV. EPSP rise times were consistent with the majority of the synapses being located on basal dendrites; this was confirmed by full anatomical reconstructions of a subset of connected pairs. Over a third of the connections could be described using a quantal model that assumed simple binomial statistics. Release probability (P(r)) and quantal size (Q), as measured at the somatic recording site, showed considerable heterogeneity between connections. However, across the population of connections, values of P(r) and Q for individual connections were positively correlated with one another. This correlation also held for inputs to layer 5 pyramidal neurons from both layer 2/3 and neighboring layer 5 pyramidal neurons, suggesting that during development of cortical connections presynaptic and postsynaptic strengths are dependently scaled. For 2/3 to 2/3 connections, mean EPSP amplitude was correlated with both Q and P(r) values but uncorrelated with N, the number of functional release sites mediating the connection. The efficacy of a cortical connection is thus set by coordinated presynaptic and postsynaptic strength.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex.J Physiol. 1997 Apr 15;500 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):409-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022031. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9147328 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic properties of excitatory synaptic connections involving layer 4 pyramidal cells in adult rat and cat neocortex.Cereb Cortex. 2007 Sep;17(9):2190-203. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhl126. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Cereb Cortex. 2007. PMID: 17116652
-
Effect, number and location of synapses made by single pyramidal cells onto aspiny interneurones of cat visual cortex.J Physiol. 1997 May 1;500 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):689-713. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022053. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9161986 Free PMC article.
-
The morphology of excitatory central synapses: from structure to function.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Nov;326(2):221-37. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0288-z. Epub 2006 Aug 24. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16932936 Review.
-
Analysis and comparison of morphological reconstructions of hippocampal field CA1 pyramidal cells.Hippocampus. 2005;15(3):302-15. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20051. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 15490464 Review.
Cited by
-
Excitatory neuronal connectivity in the barrel cortex.Front Neuroanat. 2012 Jul 11;6:24. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2012.00024. eCollection 2012. Front Neuroanat. 2012. PMID: 22798946 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous reallocation of presynaptic efficacy in recurrent excitatory circuits adapting to inactivity.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Dec 18;15(2):250-7. doi: 10.1038/nn.3004. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22179109 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of trans-synaptic nanocolumns, a modulator of synaptic transmission.Front Comput Neurosci. 2022 Sep 28;16:969119. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2022.969119. eCollection 2022. Front Comput Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36249484 Free PMC article.
-
Fear learning induces synaptic potentiation between engram neurons in the rat lateral amygdala.Nat Neurosci. 2024 Jul;27(7):1309-1317. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01676-6. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Nat Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38871992 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Effects of Neuronal Activity on Structural Plasticity.Front Neuroanat. 2016 Jun 28;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2016.00075. eCollection 2016. Front Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 27445713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Dewey DE, Harrington DA, Fyffe RE. Cell-type specific organization of glycine receptor clusters in the mammalian spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1997;379:150–170. - PubMed
-
- Atwood HL, Marin L. Ultrastructure of synapses with different transmitter-releasing characteristics on motor axon terminals of a crab, Hyas areneas. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;231:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. Quantal analysis of EPSCs recorded from small numbers of synapses in hippocampal cultures. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:1145–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
