BAMBI (bone morphogenetic protein and activin membrane-bound inhibitor) reveals the involvement of the transforming growth factor-beta family in pain modulation
- PMID: 20107078
- PMCID: PMC6633776
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2584-09.2010
BAMBI (bone morphogenetic protein and activin membrane-bound inhibitor) reveals the involvement of the transforming growth factor-beta family in pain modulation
Abstract
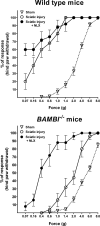
Transforming growth factors-beta (TGF-betas) signal through type I and type II serine-threonine kinase receptor complexes. During ligand binding, type II receptors recruit and phosphorylate type I receptors, triggering downstream signaling. BAMBI [bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and activin membrane-bound inhibitor] is a transmembrane pseudoreceptor structurally similar to type I receptors but lacks the intracellular kinase domain. BAMBI modulates negatively pan-TGF-beta family signaling; therefore, it can be used as an instrument for unraveling the roles of these cytokines in the adult CNS. BAMBI is expressed in regions of the CNS involved in pain transmission and modulation. The lack of BAMBI in mutant mice resulted in increased levels of TGF-beta signaling activity, which was associated with attenuation of acute pain behaviors, regardless of the modality of the stimuli (thermal, mechanical, chemical/inflammatory). The nociceptive hyposensitivity exhibited by BAMBI(-/-) mice was reversed by the opioid antagonist naloxone. Moreover, in a model of chronic neuropathic pain, the allodynic responses of BAMBI(-/-) mice also appeared attenuated through a mechanism involving delta-opioid receptor signaling. Basal mRNA and protein levels of precursor proteins of the endogenous opioid peptides proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and proenkephalin (PENK) appeared increased in the spinal cords of BAMBI(-/-). Transcript levels of TGF-betas and their intracellular effectors correlated directly with genes encoding opioid peptides, whereas BAMBI correlated inversely. Furthermore, incubation of spinal cord explants with activin A or BMP-7 increased POMC and/or PENK mRNA levels. Our findings identify TGF-beta family members as modulators of acute and chronic pain perception through the transcriptional regulation of genes encoding the endogenous opioids.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TGF-β and opioid receptor signaling crosstalk results in improvement of endogenous and exogenous opioid analgesia under pathological pain conditions.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 9;34(15):5385-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4405-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24719115 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β in normal nociceptive processing and pathological pain models.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Feb;45(1):76-86. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8221-1. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22125199 Review.
-
Deletion of the CCK2 receptor gene reduces mechanical sensitivity and abolishes the development of hyperalgesia in mononeuropathic mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Sep;20(6):1577-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03619.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15355324
-
Silencing of TGF-beta signalling by the pseudoreceptor BAMBI.Nature. 1999 Sep 30;401(6752):480-5. doi: 10.1038/46794. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10519551
-
Expression and Function of BMP and Activin Membrane-Bound Inhibitor (BAMBI) in Chronic Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 9;24(4):3473. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043473. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TGF-β and opioid receptor signaling crosstalk results in improvement of endogenous and exogenous opioid analgesia under pathological pain conditions.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 9;34(15):5385-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4405-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24719115 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) as a potent negative regulator of adipogenesis and modulator of autocrine/paracrine adipogenic factors.Diabetes. 2012 Jan;61(1):124-36. doi: 10.2337/db11-0998. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22187378 Free PMC article.
-
Activins and Inhibins: Roles in Development, Physiology, and Disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Jul 1;8(7):a021881. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021881. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27328872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variation in iron metabolism is associated with neuropathic pain and pain severity in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 21;9(8):e103123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103123. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25144566 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β in normal nociceptive processing and pathological pain models.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Feb;45(1):76-86. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8221-1. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22125199 Review.
References
-
- Bester H, Beggs S, Woolf CJ. Changes in tactile stimuli-induced behavior and c-Fos expression in the superficial dorsal horn and in parabrachial nuclei after sciatic nerve crush. J Comp Neurol. 2000;428:45–61. - PubMed
-
- Böttner M, Krieglstein K, Unsicker K. The transforming growth factor-βs: structure, signalling, and roles in nervous system development and functions. J Neurochem. 2000;75:2227–2240. - PubMed
-
- Bouret S, Chuoi-Mariot MT, Prevot V, Croix D, Takumi T, Jegou S, Vaudry H, Beauvillain JC, Mitchell V. Evidence that TGF beta may directly modulate POMC mRNA expression in the female rat arcuate nucleus. Endocrinology. 2001;142:4055–4065. - PubMed
-
- Bourquin AF, Süveges M, Pertin M, Gilliard N, Sardy S, Davison AC, Spahn DR, Decosterd I. Assessment and analysis of mechanical allodynia-like behavior induced by spared nerve injury (SNI) in the mouse. Pain. 2006;122:14.e1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
